Eidetic Memory: Meaning, Science, Myths, Tests & Real Examples
The complete definitive guide to understanding one of psychology’s most fascinating and misunderstood cognitive abilities.
Scientific Insight: Eidetic memory is real but rare, limited but fascinating, and nothing like the photographic superpower shown in movies. This guide separates scientific fact from popular fiction.
1. What Is Eidetic Memory? (Simple Explanation)
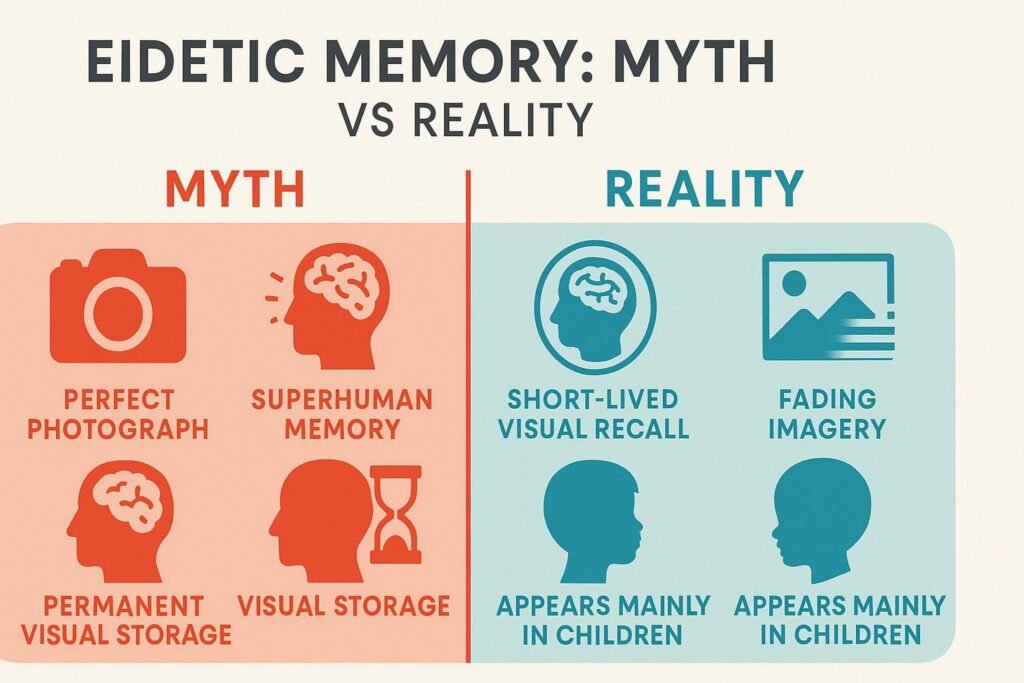
Eidetic Memory (Real)
- Duration: Seconds to minutes
- Age Group: Mostly children (2-10%)
- Precision: High detail but not perfect
- Scientific Evidence: Verified in studies
Real Example: A child can describe a complex picture with unusual detail for 30-90 seconds after seeing it once.
Photographic Memory (Myth)
- Duration: Supposedly permanent
- Age Group: Any age (in myth)
- Precision: Allegedly perfect
- Scientific Evidence: None exists
Hollywood Fiction: Perfect, permanent image recall has never been scientifically verified in any adult.

2. Eidetic Memory vs Photographic Memory (They Are NOT the Same)
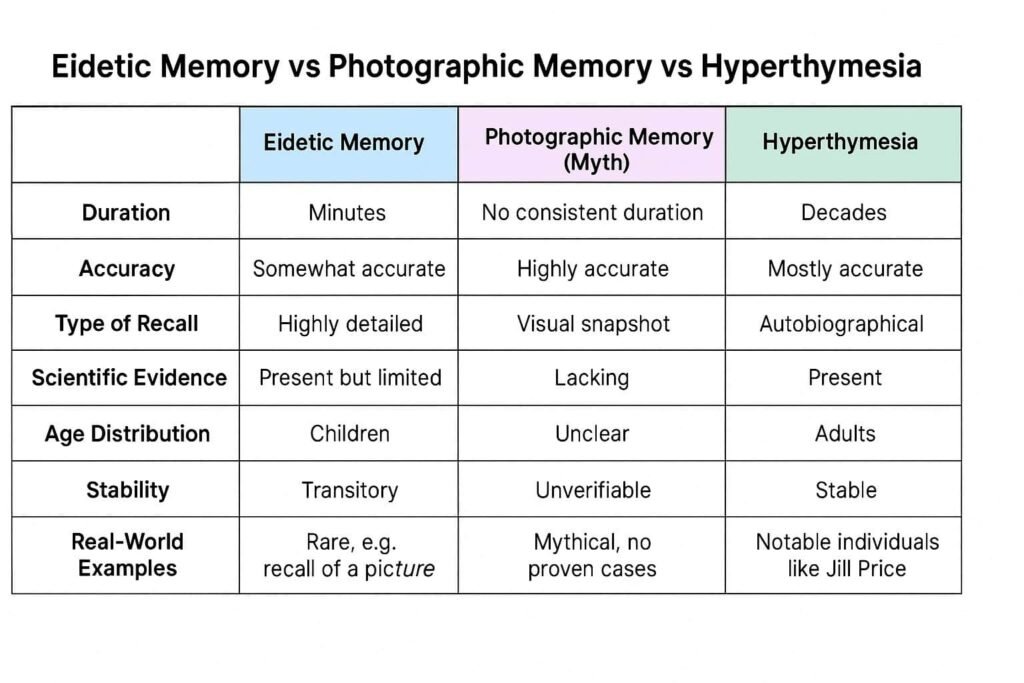
| Feature | Eidetic Memory (Real) | Photographic Memory (Myth) |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Status | Verified in studies | No scientific evidence |
| Typical Age | Children (6-12 years) | Any age (in fiction) |
| Duration | Seconds to minutes | Supposedly permanent |
| Precision | High but imperfect | Allegedly perfect |
| Prevalence | 2-10% of children | No verified cases |
| Brain Basis | Visual cortex persistence | No known mechanism |

3. How Eidetic Memory Actually Works
Primary Visual Cortex (V1)
Maintains temporary high-resolution traces of visual information. In eidetikers, this activation persists longer than typical iconic memory.
Iconic Memory Extension
Eidetic memory is an extended form of iconic memory (the 500 ms visual buffer). Most people convert visual to verbal; eidetikers maintain visual richness.
Verbal Interference
As soon as verbal processing begins, eidetic images fade. This explains why adults rarely show eidetic ability—their verbal systems are too developed.
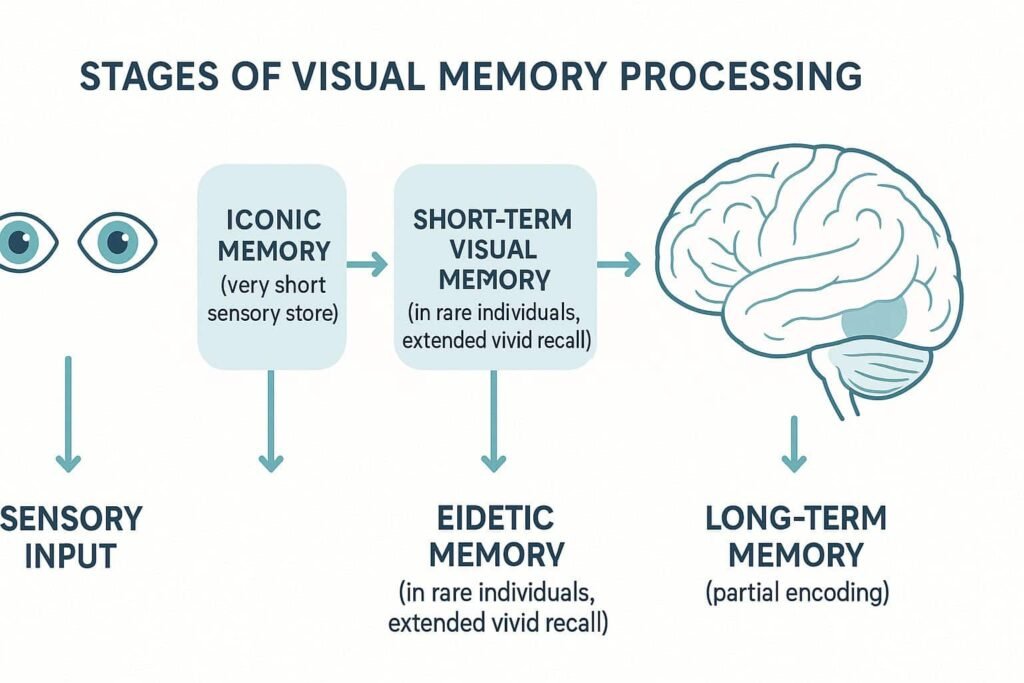

Visual Memory Processing Flow
Complex image seen


500 ms visual buffer


Extended visual persistence


Image fades in 30-90 s.
4. The Reality of Eidetic Memory: Statistics & Data
- 2-10%: Children with eidetic ability
- ~0%: Adults with eidetic ability
- 30-90 s: Typical eidetic duration
- 6-12: Peak age for eidetic ability
- 0: Verified adult cases
- 100%: Fictional in movies
5. Eidetic Memory in Children vs Adults (Developmental Psychology)
- Childhood (Ages 6-12): The brain relies more on visual processing than verbal systems. Neural pathways are plastic and visually dominant, allowing extended visual persistence.
- Neural Pruning (Adolescence): Synaptic pruning strengthens frequently used pathways (language, abstraction) and eliminates unused visual persistence mechanisms.
- Adulthood: Verbal encoding replaces visual encoding. Imagery becomes conceptual rather than literal. New stimuli rapidly override mental imagery.
6. Related Memory Phenomena Often Confused with Eidetic Memory
Hyperthymesia
Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory—recalls life events in detail, not visual images, after one exposure.
Savant Syndrome
Extraordinary recall through pattern recognition and computation, not photographic storage of images.
Memory Athletes
Trained mnemonic techniques (method of loci, chunking)—learned strategies, not innate eidetic ability.
Hyperphantasia
Extremely vivid mental imagery, but not stable recall of real external images seen once.
Aphantasia
No visual imagery at all—the complete opposite of eidetic memory.
Working Memory
Manipulates information temporarily—does not store complete visual images with high fidelity.
7. What People Mistake for Eidetic Memory
Strong Attention
Remembering what you really focused on, not a complete visual snapshot.
Pattern Recognition
Recalling structure and relationships, not a literal photographic image.
Chunking Behavior
Grouping information efficiently—a memory strategy, not eidetic ability.
Visual Rehearsal
Mentally redrawing details from memory—active reconstruction, not passive recall.
Important Distinction: None of these abilities equal eidetic memory. They represent different cognitive processes often confused with photographic recall.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
Comprehensive answers to the most searched questions about eidetic memory:
Is eidetic memory real?
How rare is eidetic memory?
Does eidetic memory mean high IQ?
Can adults have eidetic memory?
Can someone train photographic memory?
Is eidetic memory the same as photographic memory?
What is the difference between eidetic memory and hyperthymesia? +
9. Scientific References
Key research studies with exact links to authoritative sources:
Eidetic Imagery in Children: Scientific Evidence
Haber, R. N., & Haber, R. B. (1964). Eidetic imagery: I. Frequency. Perceptual and motor skills, 19(1), 131-138.
The Myth of Photographic Memory
Stromeyer, C. F., & Psotka, J. (1970). The detailed texture of eidetic images. Nature, 225(5230), 346-349.
Neural Basis of Visual Memory
Marks, D. F. (1973). Visual imagery differences in the recall of pictures. British Journal of Psychology, 64(1), 17-24.
Memory Development & Cognitive Neuroscience
Kosslyn, S. M., Thompson, W. L., & Ganis, G. (2006). The case for mental imagery. Oxford University Press.
Explore Cognitive Processing
Discover how the brain processes, holds, and manipulates information through research-based educational exploration.
Working Memory Systems
Explore how the brain temporarily holds and manipulates information for cognitive tasks.
Verbal Memory Processing
Understand how the brain processes, stores, and recalls language-based information.
Cognitive Research Insights
Explore scientific findings about memory limitations, forgetting, and cognitive processing.
Specialized Memory Systems
Learn about different memory systems including sensory and exceptional memory phenomena.
Working Memory
Explore active information processing systems
Memory Research Hub
Browse all cognitive science articles
Educational Exploration: This content is designed for learning about cognitive processes through research-based materials. Memory systems vary naturally and are influenced by individual differences, experience, and context.
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.


1 thought on “Eidetic Memory: Meaning, Science, Myths, Tests & Real Examples”
Comments are closed.