
Benefits of the Chimp Test: What It Reveals About Memory, Attention & Human Cognition
The chimp test is a rapid visual-memory task made famous by Kyoto University's research showing that young chimpanzees can recall flashing numbers faster and more accurately than adult humans. But beyond the viral videos, this test carries deep scientific value.
Scientific Insight: This test helps researchers compare species, understand the limits of human attention, and explore how memory evolved along different paths in primates. Discover all the benefits—for scientists, educators, and humans who take the test.
Test Your Memory Like a Chimp
Experience the cognitive challenge that reveals how your visual working memory compares to chimpanzees. The full interactive version provides accurate timing, scoring, and progressive difficulty levels.
The complete test includes 9 numbers, 210ms exposure time, accuracy tracking, and comparison data with chimpanzee performance.
1. Scientific Benefits of the Chimp Test
The chimp test reveals insights that no other simple cognitive experiment can. While humans excel in language and abstract reasoning, chimps demonstrate extreme speed in visual-spatial memory.
Chimps encode screens in single glances—"snapshot" memory that shows upper limits of rapid encoding and demonstrates eidetic-like abilities in juveniles.
Tests ability to remember item locations—a key survival trait for locating fruits and predators. Shows differences in parietal lobe specialization across species.
Chimps perform fast AND accurate, challenging assumptions about cognitive hierarchy and revealing neural circuits optimized for rapid processing.
Humans have 200–500ms "blind spot" for second targets; chimps barely experience this, highlighting evolutionary trade-offs in attention systems.
Chimp vs Human Memory Processing
| Feature | Chimpanzees | Humans |
|---|---|---|
| Encoding Style | Parallel (whole array) | Serial (item by item) |
| Processing Speed | 200-300ms optimal | 500-1000ms optimal |
| Attentional Blink | Minimal (50-100ms) | Significant (200-500ms) |
| Visual Cortex Activation | Stronger V1/V2 areas | Stronger prefrontal areas |
| Evolutionary Priority | Visual speed & spatial accuracy | Language & abstract reasoning |
2. Benefits for Humans Taking the Test
Most discussions focus on chimps, but humans gain significant insights from taking the chimp test themselves.
Your score reveals encoding speed, item retention capacity, and natural visual memory span—more precise than most online memory tests.
Low scores may indicate slow encoding, weak spatial recall, or high attentional blink susceptibility—valuable for students, gamers, and ADHD individuals.
Repeated testing improves encoding speed, stimulus detection, visual chunking, and attentional endurance through gamified cognitive training.
Trains brain to adapt faster, process visual patterns, and handle rapid sequences—improving performance in fast-paced environments.
Ready to Test Your Memory?
Take the full Chimp Memory Test to get accurate measurements of your visual working memory capacity and see how you compare to chimpanzee performance.
Launch Full Test at MemoryRushQuantitative Performance Differences
Research-backed statistics showing chimp-human cognitive differences:
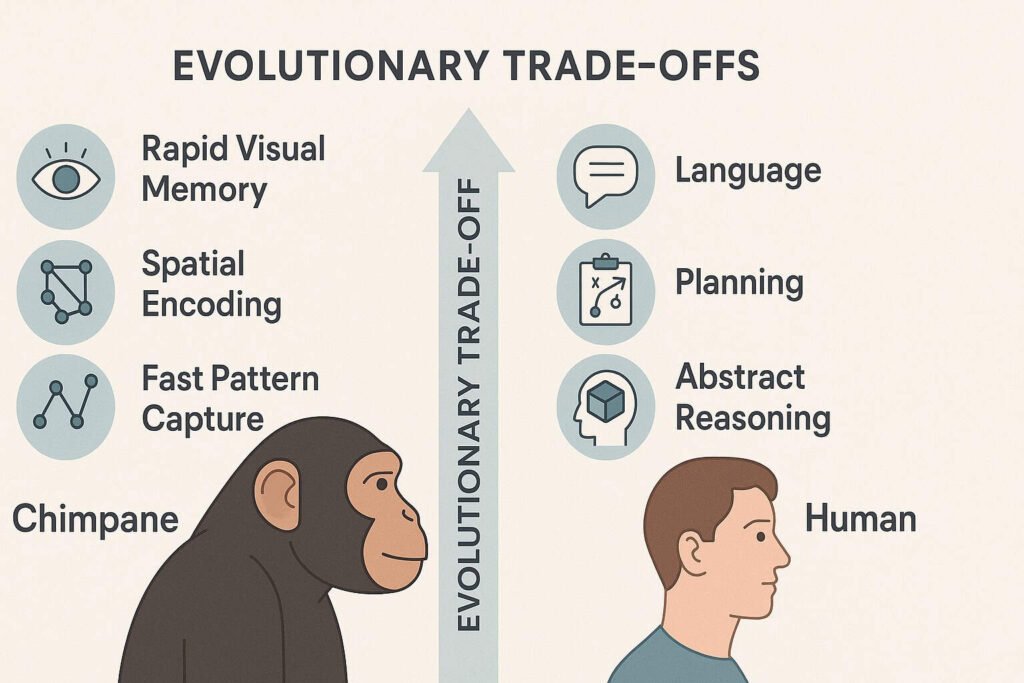
Evolutionary Timeline: Cognitive Trade-Offs
How humans and chimps developed different cognitive strengths:
Chimps evolved rapid visual processing for navigating dense forests, detecting predators, and locating food sources—optimizing for survival speed.
Humans invested cognitive resources in language development, abstract reasoning, and social planning—sacrificing some visual processing speed for complex communication.
Chimps maintained parallel processing of entire visual arrays. Humans developed serial processing optimized for language and sequential reasoning tasks.
Today, chimps excel at rapid visual memory while humans dominate symbolic thought, long-term planning, and complex problem-solving—different evolutionary optimizations.
Test Your Evolutionary Adaptations
Discover where you fall on the spectrum between rapid visual processing (chimp-like) and complex reasoning (human-like) by taking the scientific Chimp Memory Test.
Take Scientific AssessmentFrequently Asked Questions
Comprehensive answers to common questions about the chimp test and its benefits:
Get Your Questions Answered
Take the full Chimp Memory Test to experience the cognitive challenge firsthand and get personalized insights into your visual working memory capabilities.
Experience the Test & Get AnswersScientific References
Key research studies supporting the cognitive science of chimp test benefits:
Inoue, S., & Matsuzawa, T. (2007). Working memory of numerals in chimpanzees. Current Biology, 17(23), R1004-R1005.
View Original StudyMatsuzawa, T. (2009). Symbolic representation of number in chimpanzees. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 19(1), 92-98.
View Original StudySherwood, C. C., & Gómez-Robles, A. (2017). Brain plasticity and human evolution. Annual Review of Anthropology, 46, 399-419.
View Original StudyMacLean, E. L., et al. (2012). How does cognition evolve? Phylogenetic comparative psychology. Animal Cognition, 15(2), 223-238.
View Original Study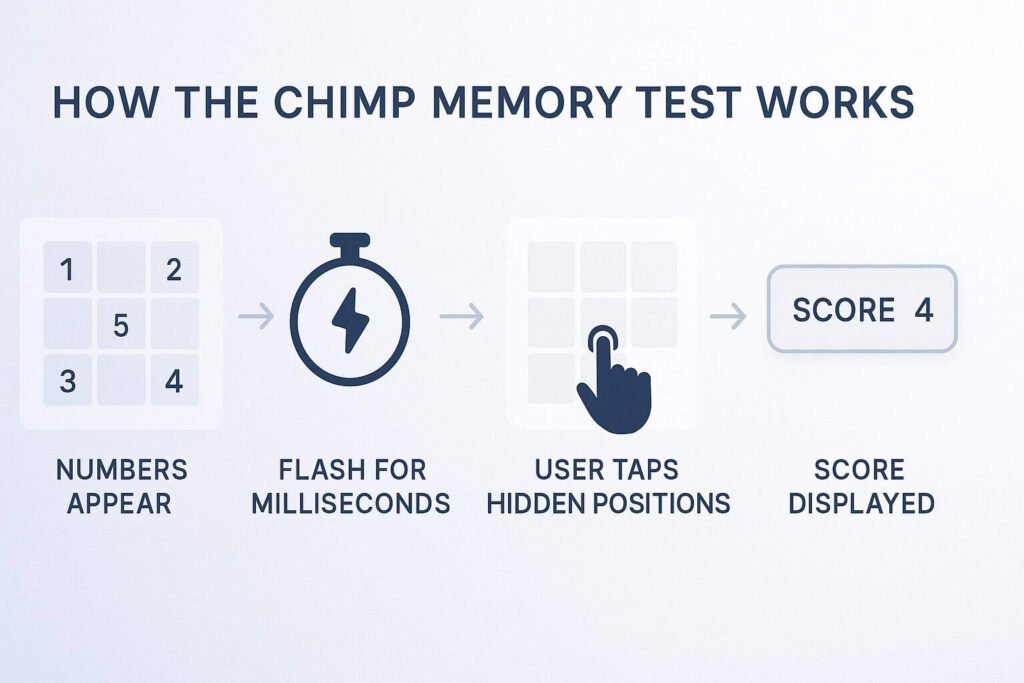

Explore Memory Research
MemoryRush offers research-inspired educational content designed for learning and self-exploration. Not a medical assessment.
Chimp Test Research
Explore the cognitive science behind chimpanzee memory studies and what they reveal about primate cognition.
Scientific Insights
Understand what memory research reveals about attention, perception, and cognitive processing in primates.
Learning & Practice
Educational guides for understanding and practicing memory techniques inspired by cognitive research.
Note: This content is for educational self-exploration and learning purposes only. It is not a medical or psychological assessment. Results are based on practice and vary naturally between individuals.
Browse All Chimp Test Content →Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.

