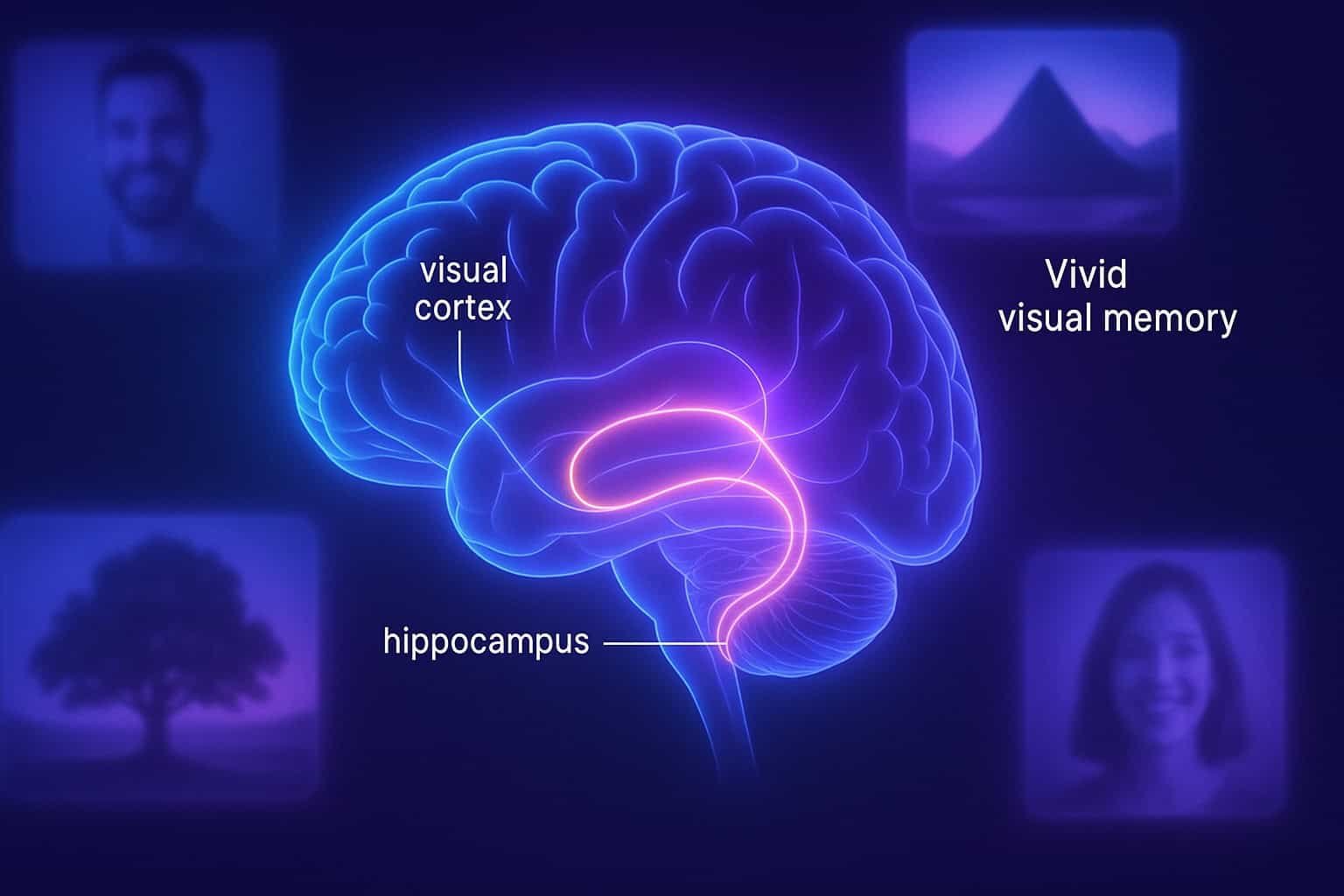
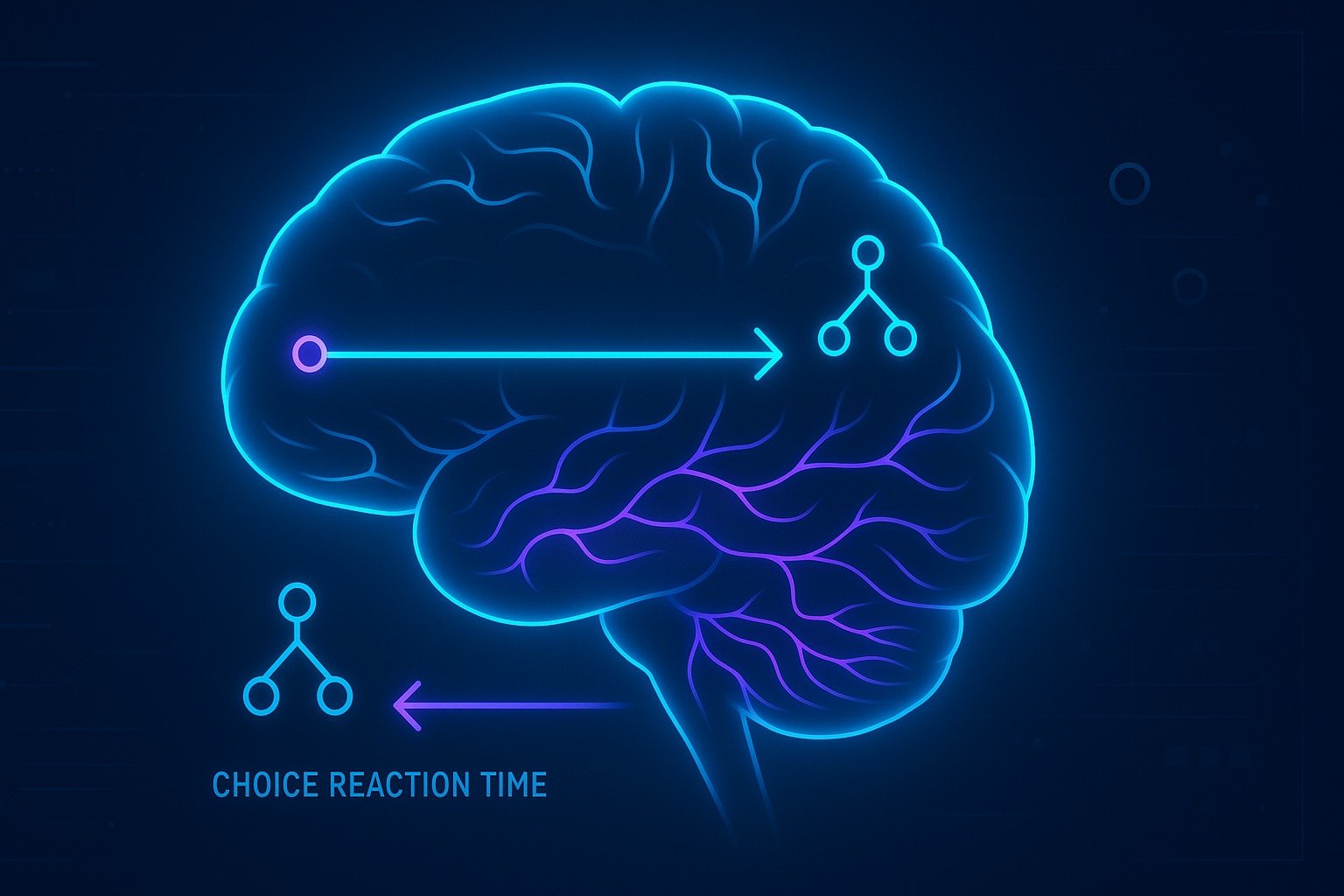
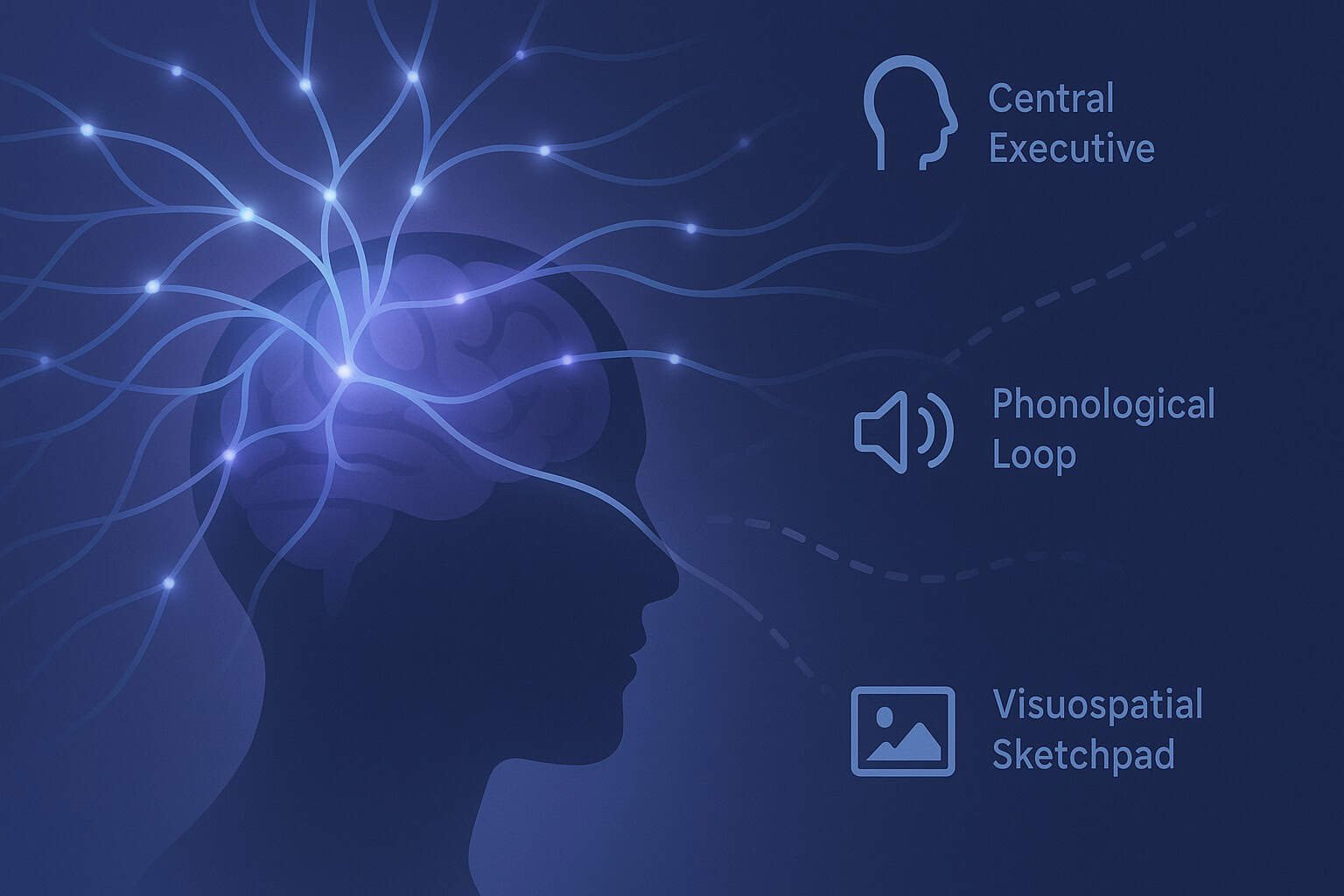
Difference Between Low-Level and High-Level Pattern Recognition
Low-level pattern recognition extracts raw sensory features, while high-level recognition interprets them into meaningful concepts. This guide explains how the brain and AI systems transform edges and shapes into objects, categories, and understanding.