
Chimpanzee Eidetic Memory Study
Why Chimpanzee Memory Puzzles Scientists
For decades, scientists believed humans were unmatched in symbolic reasoning and higher cognitive functions. But in 2007, a stunning experiment from Kyoto University shocked the world: young chimpanzees performed a visual memory task faster and more accurately than trained adult humans.
In moments when numbers flashed on the screen for as little as 210 milliseconds—faster than a human eye blink—these chimpanzees not only perceived the digits but also recalled their positions perfectly. Humans, including university students, struggled badly. This article provides the complete explanation behind this phenomenon.
Three Types of Visual Memory
Mythical Perfect Recall
Perfect storage of visual information with infinite detail. Never scientifically confirmed in any species. A popular misconception rather than a documented phenomenon.
High-Resolution Short-Term
Enhanced visual recall lasting seconds after stimulus removal. Most common in young children. Fades as language and abstraction develop. Not perfect but exceptionally detailed.
Speed-Optimized Capture
Rapid visual encoding with minimal filtering. Exceptional spatial recall under time pressure. Evolved for survival in complex 3D forest environments requiring quick visual processing.


Neural Architecture Comparison
Brain Differences Behind the Performance Gap
| Brain Region | Chimpanzee Advantage | Human Specialization |
|---|---|---|
| Posterior Parietal Cortex | Enhanced spatial mapping and rapid visual capture | Visual Processing |
| Impact on Task | Chimps excel at spatial position recall under time pressure | |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Less inhibitory filtering of visual input | Information Filtering |
| Impact on Task | Chimps capture visual arrays with minimal processing delay | |
| Visual Cortex (V1-V4) | Optimized for rapid pattern recognition | Pattern Processing |
| Impact on Task | Chimps process visual arrays faster for immediate recall | |
| Temporal Lobe | Efficient spatial memory encoding | Memory Encoding |
| Impact on Task | Chimps remember locations better than abstract meanings | |
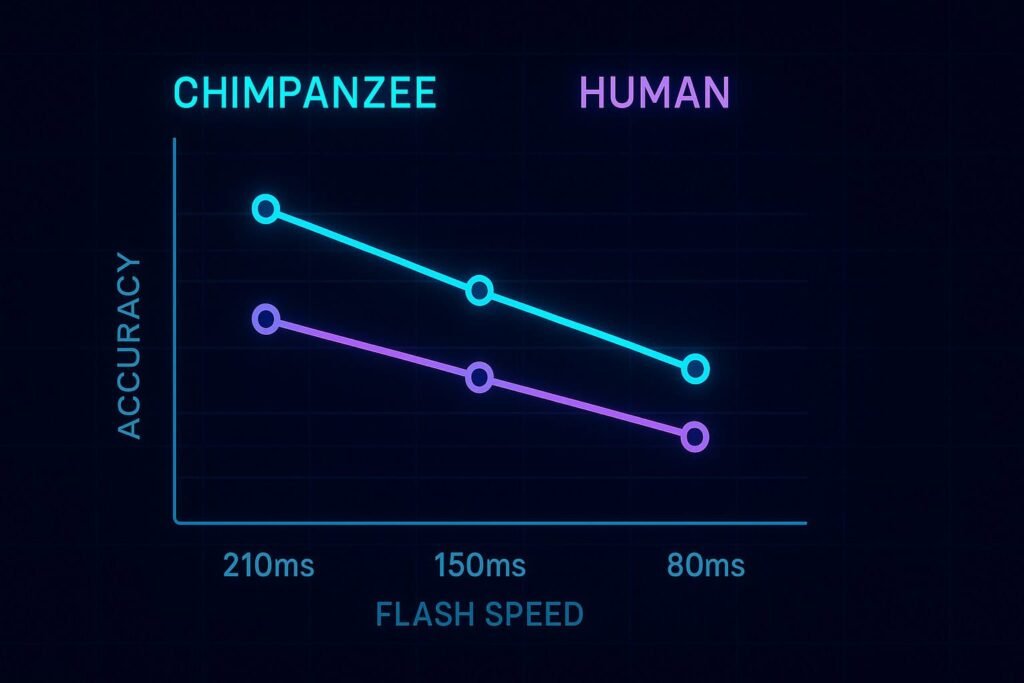

Performance Comparison: Chimps vs Humans
Young Chimpanzees
90-95%
Accuracy at ms
• Nearly perfect recall
• Rapid response times
• Minimal training required
• Natural ability observed
University Students
30-40%
Accuracy at ms
• Significant memory failures
• Slower responses
• Months of training needed
• Performance collapses at speed
Scientific References & External Sources
- Kyoto University Primate Research Institute – Ai Project Overview. https://www.pri.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ai/en/
- Cell Press—Working—Working Memory of Numerals in Chimpanzees (Inoue & Matsuzawa, 2007). 2007). https://www.cell.com/current-biology/pdf/S0960-9822(07)02436-8.pdf
- Scientific American—Chimps—Chimps Outplay Humans in Brain Games. Games. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/chimps-outplay-humans-in-brain-games/
- New Scientist—Chimpsutperform Humans at Memory Task. https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn12993-chimps-outperform-humans-at-memory-task/
Test Your Memory Against the Chimps
Explore the Chimp Memory Test, understand why chimpanzees outperform humans in rapid recall, and learn how to improve your own visual memory.
Take the Chimp Test
Challenge your working memory by remembering fast-changing number patterns, inspired by the famous chimpanzee Ayumu experiment.
Play GameLearn About the Test
Learn what the Chimp Test measures, how it relates to visual-spatial working memory, and why humans struggle with ultra-fast recall.
Read MoreImprove Your Score
Practical techniques like chunking, pattern grouping, and attention control to help you improve performance over time.
Improve SkillsChimp vs Human Memory
A clear comparison of chimpanzee and human cognitive strengths, including evolutionary trade-offs in memory and reasoning.
CompareThe Original Experiment
Explore the Kyoto University study that revealed chimpanzees’ exceptional short-term visual memory.
Explore StudyAttention Blink Effect
Learn why human brains miss rapid visual stimuli and how attention blink limits performance in fast memory tasks.
Learn ScienceTouheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.


1 thought on “Chimpanzee Eidetic Memory Study”
Comments are closed.