Difference Between Low-Level and High-Level Pattern Recognition
Introduction: Why Pattern Recognition Exists in Levels
The human brain doesn’t process complex scenes as single units. Instead, it breaks them down into hierarchical layers that build from simple to complex:
Low-level recognition extracts raw features such as edges, curves, colors, and textures
High-level recognition interprets those features into meaningful concepts such as faces, objects, emotions, and intentions
🧠 Core Insight: The human brain and modern AI both rely on hierarchical pattern recognition. This multi-layer structure provides speed, accuracy, energy efficiency, abstraction, and predictive ability—without which neither biological nor artificial systems could process complex environments.
⚡ Why Hierarchy Matters: This layered approach provides speed (parallel processing), accuracy (error correction at each level), energy efficiency (only complex patterns require deep processing), abstraction (generalization from specifics), and predictive ability (anticipation based on partial information).
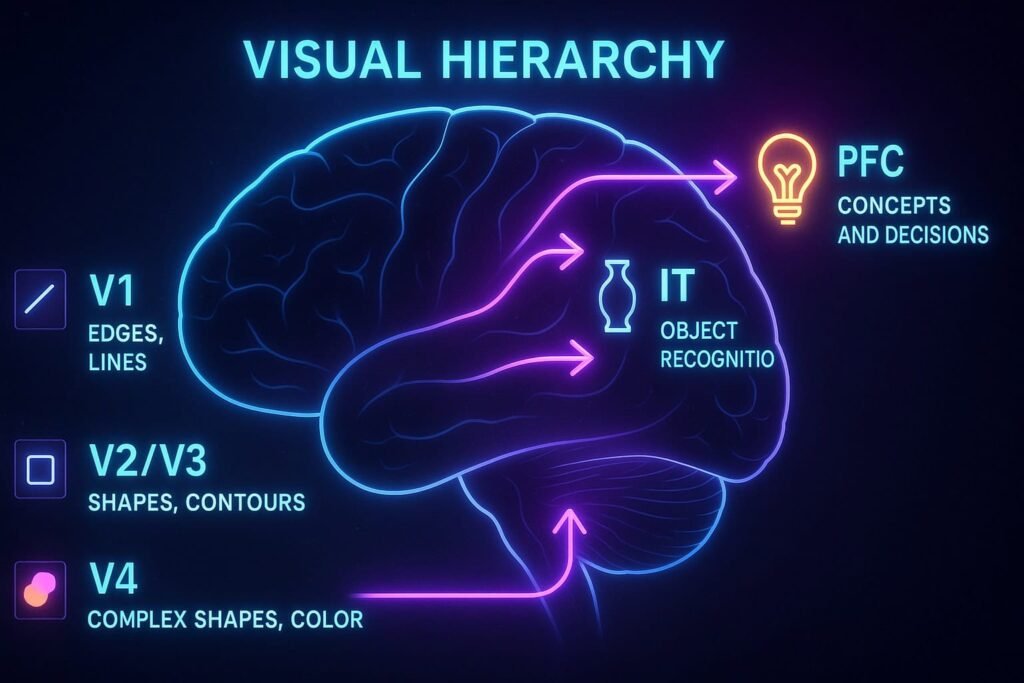

2. What Low-Level Pattern Recognition Actually Is
Neuroscience Definition
In the brain, low-level recognition happens in V1–V2 of the visual cortex, which detects:
Edges and contours
Orientation and angles
Contrast and brightness
Basic motion detection
Color gradients
These features have no meaning yet—only structure.
Machine Learning Definition
In computer vision, low-level recognition equals:
Pixel-level filters
Edge detection algorithms
Texture extraction
Gradient calculations
Contrast maps
These occur in the first layers of a CNN, before any object understanding.
Key Characteristics of Low-Level Recognition
Fast & Automatic: Occurs without conscious effort, typically within 50-100 ms
No Context Awareness: Processes features independently of meaning or environment
Raw Structure Only: Extracts basic building blocks without interpretation
🔍 Low-Level Examples: Seeing a vertical line, detecting motion in the periphery, distinguishing red from blue, hearing a high vs low pitch. These are the fundamental inputs that all higher processing builds upon.
3. What High-Level Pattern Recognition Is
Neuroscience Definition
High-level recognition occurs in specialized brain regions:
V4 & Inferotemporal Cortex (IT) → object categories
Fusiform Gyrus → face recognition
Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) → semantic meaning, intent, concepts
This level handles recognition, categorization, and interpretation.
Machine Learning Definition
In ML, high-level recognition means:
Concept detection and classification
Semantic embeddings
Abstract reasoning
Pattern generalization
These occur in deep layers of neural networks.
Key Characteristics of High-Level Recognition
Context-Dependent: Meaning changes based on situation and previous knowledge
Meaningful & Goal-Driven: Linked to objectives, intentions, and semantic understanding
Abstract & Generalized: Works with concepts rather than specific instances
🔍 High-Level Examples: Recognizing a friend’s face instantly, understanding a complex scene (a classroom, a protest, a kitchen), identifying subtle emotions in facial expressions, and reading a word and comprehending its nuanced meaning.
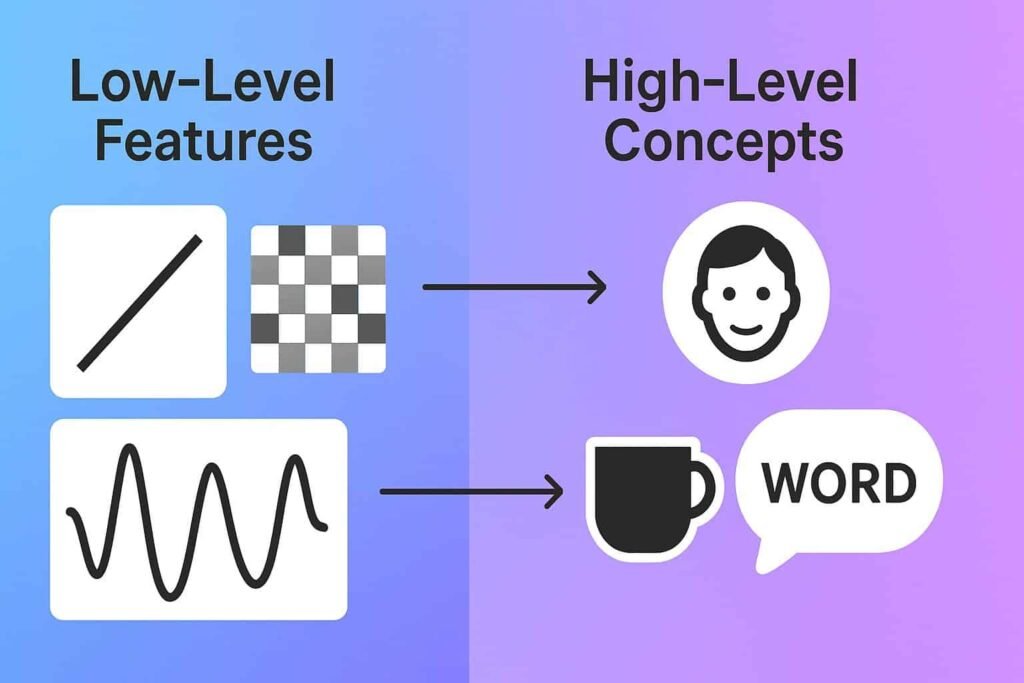

4. Low-Level vs High-Level Pattern Recognition (Side-by-Side Comparison)
| Feature | Low-Level Recognition | High-Level Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| What it Processes | Raw sensory features (edges, colors, lines) | Concepts & categories (faces, emotions, scenes) |
| Brain Area | V1–V2 (Early visual cortex) | IT Cortex, PFC (Higher-order areas) |
| Meaning? | No inherent meaning | Yes, semantic interpretation |
| Context-Dependent? | No, operates independently | Yes, heavily influenced by context |
| Speed | Very fast (50-100 ms) | Slower but smarter (200-500 ms+) |
| ML Analogy | Early CNN filters | Deep semantic layers |
5. The Hierarchical Pipeline: How Low-Level Feeds High-Level
Step 1: V1 → Edge Detection
Extracts basic edges, orientation, and contrast from raw visual input. The foundation of all visual processing.
Step 2: V2/V3 → Contour & Shape Formation
Combines edges into contours and simple shapes. Begins grouping related features.
Step 3: V4 → Color & Complex Shapes
Processes color information and integrates shapes into more complex forms. Adds visual richness.
Step 4: IT Cortex → Object & Category Recognition
Identifies objects and categorizes them based on learned templates. Where “seeing” becomes “recognizing.”
Step 5: PFC → Meaning, Intention & Prediction
Assigns semantic meaning, interprets intentions, and predicts future patterns based on context and goals.
⚡ CNN Analogy: Convolutional Neural Networks mimic this exact hierarchy: Layer 1 → edges, Layer 2 → shapes, Layer 3 → textures, Layer 5+ → objects, final layer → labels. A perfect parallel to human visual processing.
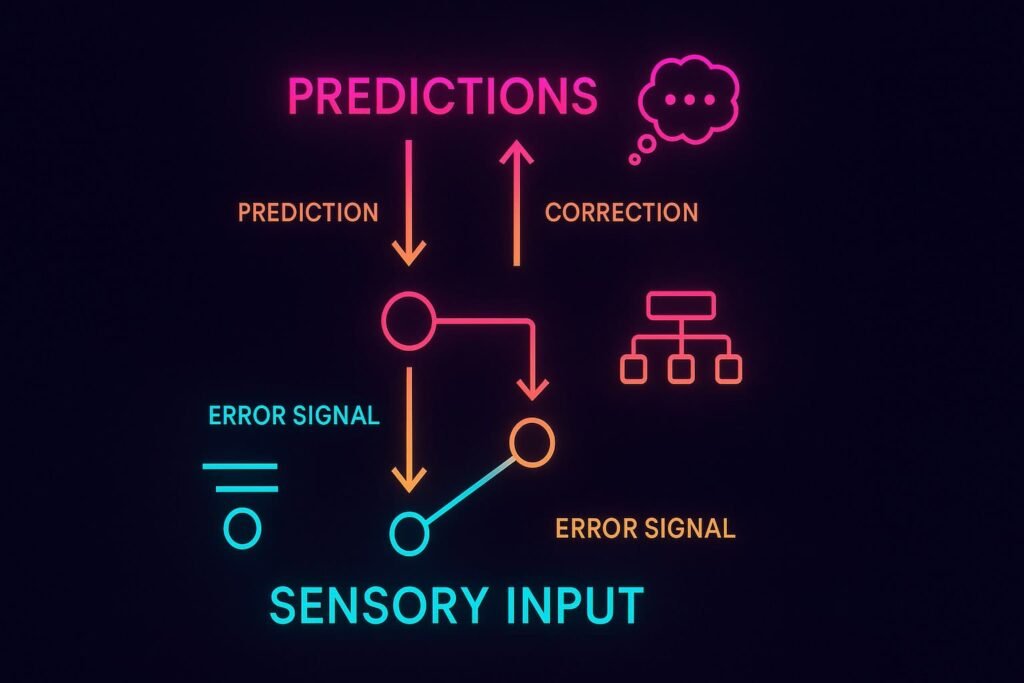

6. Real-World Human & AI Examples
Human Examples
Low-Level: Edge Detection—Noticing the diagonal line of a roof against the sky
Low-Level: Motion Detection—Detecting movement in peripheral vision in dim light
High-Level: Face Recognition—Instantly recognizing a friend in a crowded room
High-Level: Emotion Interpretation—Understanding sarcasm or subtle emotional cues
AI Examples
Low-Level: Sobel Edge Detection—Computer vision algorithm extracting edges from pixels
Low-Level: Gabor Filters—Mathematical filters mimicking V1 neuron responses
High-Level: YOLO Object Detection—Real-time identification and classification of multiple objects
High-Level: GPT Semantic Embeddings—Understanding word meaning and contextual relationships
7. Common Misconceptions About Pattern Recognition Levels
“Low-level = simple and useless”
It is foundational; without accurate edge detection, no object recognition would be possible. Low-level processing provides the raw materials for all higher cognition.
“High-level = intelligence only”
High-level processes rely completely on the accuracy of low-level detection. Both levels are essential—one provides data, the other provides meaning.
“AI sees exactly like humans.”
AI mimics the hierarchical structure but lacks biological emotion, consciousness, and true understanding. It’s architecture-inspired, not biology-equivalent.
“Low-level and high-level are separate.”
They are inseparable parts of a continuous processing hierarchy. Information flows bidirectionally between levels in predictive coding loops.
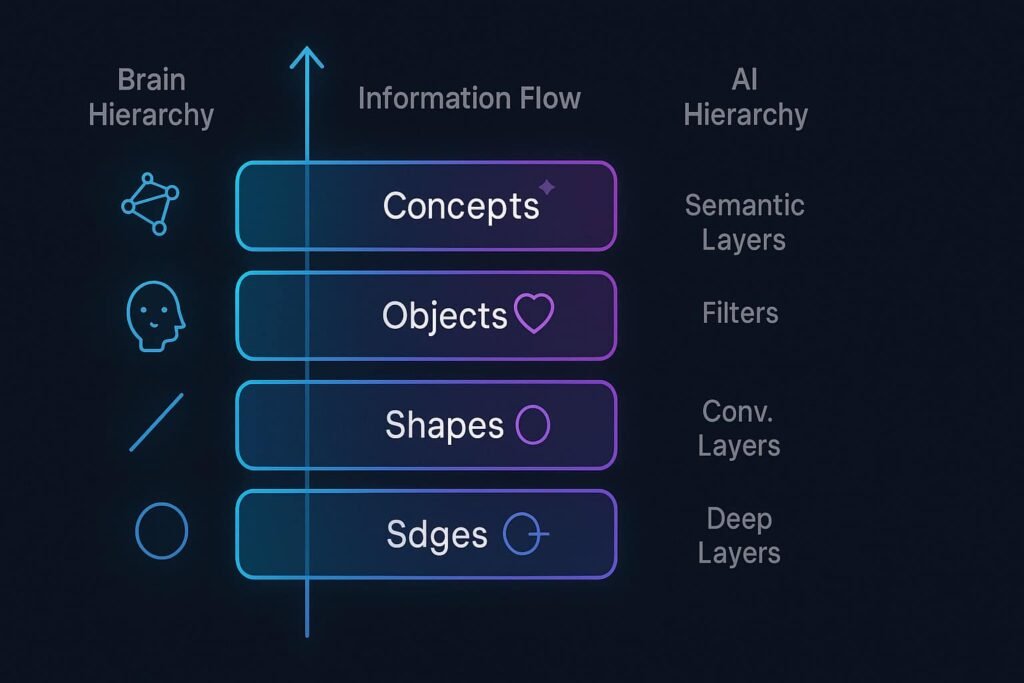

8. Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of low-level pattern recognition?
Low-level recognition includes detecting edges, colors, brightness, or simple shapes. These are raw features extracted before the brain assigns meaning or context.
Why is low-level vision important?
Low-level vision provides the foundational features—edges, textures, contrasts—that high-level processes rely on to identify objects and interpret scenes.
What is the main role of high-level vision?
High-level vision interprets complex information: recognizing faces, understanding scenes, and assigning semantic meaning based on context and memory.
Are low-level and high-level features processed in different brain areas?
Yes. Low-level features are processed in the early visual cortex (V1–V2), while high-level features involve areas like the inferotemporal cortex and prefrontal cortex.
How do low-level features contribute to object recognition?
Edges and contours combine into shapes, which form object templates. Without accurate low-level detection, the brain cannot reliably identify objects.
What makes high-level pattern recognition more complex?
It integrates memory, context, attention, and prediction. High-level recognition relies on linking features to concepts, categories, and goals.
How does machine learning use low-level features?
ML models extract low-level features using convolution filters or edge detectors, forming the basis for higher-level classification layers.
What is the difference between feature extraction and pattern recognition?
Feature extraction refers to capturing raw attributes (edges, curves), while pattern recognition assigns meaning by matching combinations of features to known categories.
Why is high-level pattern recognition slower than low-level?
High-level recognition requires integrating multiple features, comparing past experience, and evaluating context, making it computationally heavier.
Can low-level and high-level processing happen at the same time?
Yes. The brain processes information in parallel streams, allowing rapid feature detection while simultaneously forming predictions and interpretations.
9. One-Minute Summary
Low-Level Recognition
Edges, colors, and shapes (fast, raw, and automatic). The building blocks of perception.
High-Level Recognition
Objects, faces, meaning (contextual, abstract). Where raw data becomes understanding.
Hierarchical Architecture
Both form a layered hierarchy enabling perception, intelligence, and prediction across biology and AI.
10. Scientific References & External Sources
National Institutes of Health (NIH)—Superior Pattern Processing Article
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4141622/
Explains how human brains process and interpret patterns at different hierarchical stages. Foundation for understanding biological pattern ranking mechanisms.
MIT Picower Institute – Universal Brain Wave Frequency Patterns
https://picower.mit.edu/news/study-reveals-universal-pattern-brain-wave-frequencies
Shows how layered oscillations correspond to hierarchical feature extraction and ranking in neural processing.
Stanford University – Hidden Pattern That Drives Brain Growth
https://news.stanford.edu/stories/2020/03/hidden-pattern-brain-growth
Research describing how neuronal growth follows mathematical and hierarchical patterns mirroring computational architectures.
University College London (UCL)—Pattern Classification in Brain Activity
https://www.gatsby.ucl.ac.uk/~pelc/KulkarniMack2020.pdf
Academic comparison of pattern recognition methods in neuroscience and machine learning, highlighting hierarchical similarities.
Master Your Pattern Recognition Skills
Apply the neuroscience of pattern ranking with our specialized tools and guides. Test your abilities, understand the science, and improve your cognitive performance.
Interactive Pattern Test
Challenge your brain's pattern ranking system in real-time with scientifically designed memory tests.
Take the TestComplete Pattern Guide
Understand pattern memory fundamentals and how it differs from visual memory processing.
Read GuideTraining & Improvement
Practical strategies to enhance your pattern recognition speed, accuracy, and overall ability.
Train NowDive deeper into pattern recognition science with our comprehensive resource library:
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.


