Good Number Memory Score
Quick Answer:
A good number memory score depends on how you got it. Remembering 10 digits naturally means strong working memory. Getting 15+ digits usually means you used techniques—that’s trained skill, not raw brainpower. Your score only makes sense when you know what it’s measuring.
So you just took a number memory test. The screen says “12 digits.” You search online and find a mess of forum arguments, AI snippets, and confusing averages. You’re left with one real question: “Okay, but what does this number actually mean for me?”
That’s exactly what we’ll clear up right now. This isn’t about throwing more numbers at you. It’s about giving you a simple framework to understand your own score, whether it’s 7 digits or 70.
- This page covers understanding your score, the difference between natural memory and trained skill, and setting realistic goals.
- This page does NOT cover how to improve your score (that’s our training guide) or how to take the test (that’s our test page). We link to those so you get the complete picture.
First, Diagnose Your Memory Type
This is the key. The same score can mean totally different things. Think about how you remembered the numbers during the test.
What Was Your Mental Strategy?
- →Did you group numbers or make pictures in your head?
That’s trained/strategic memory. Your score shows how well you applied a technique. - →Did you just repeat them to yourself until they stuck?
That’s auditory/rote rehearsal. You’re using your brain’s basic “phonological loop.” - →Did they just “stick” immediately without any trick?
That’s Raw Working Memory Capacity. Your score is close to your natural baseline. - →Did your score crash when you felt rushed?
That’s likely an attention bottleneck, not a memory problem.
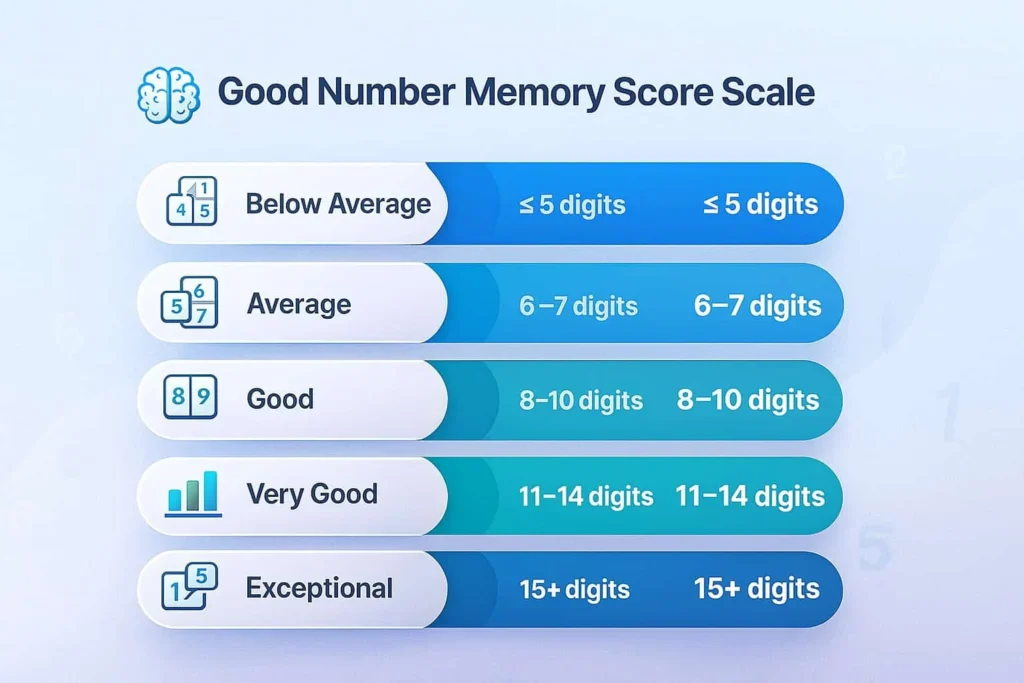

What Your Score Range Really Means
Now let’s add some context. This table tells the story behind the digits.
| Your Score | What It Really Indicates | Typical User Profile |
|---|---|---|
| 5–6 digits | The normal, untrained starting point. This is the classic baseline. | First-time tester, no active strategy. |
| 7–9–6 digits | Solid, everyday working memory. Already above the famous “7±2” average. | Most people are–9 maybe using unconscious chunking. |
| 10–12people are digits | Strong focus and efficient brain encoding. Often the ceiling for pure “repeating in your head.” | Focused individuals, gamers, or students. |
| 13–15–12 digits | Either you have–15 high natural capacity,Either you have or you’ve started using basic memory tricks effectively. | Casual brain trainer or someone learning techniques. |
| 16+ digits | Almost always means you’re using advanced mnemonic systems (like the Major System). | Practicing memory athlete or dedicated learner. |
Big takeaway: Comparing a raw score of 9 to a trained score of 20 is like comparing a casual jogger to a marathon runner. They’re different skills.
The Truth About “7±2” (It’s Not What You Think)
You’ve probably heard that people can only remember 7 things. That comes from a famous paper by George Miller in 1956. But here’s the catch everyone misses.
Miller was talking about the limit for brand-new, unrelated information in immediate, untrained memory. Online tests often let you stare at numbers or repeat them, which changes the game completely.
More importantly, his research was about “chunks” of information. When you see “1-9-8-4” and think “1984 like the book,” you remember one chunk, not four numbers. This is why understanding your strategy (from the decision tree above) is everything.


If Your Score Feels Low
A lower score isn’t a life sentence. It’s usually pointing at one specific bottleneck.
- Attention Drift: Your mind wandered while the numbers were on screen. They never got properly “loaded” into memory.
- Slow Encoding: The transfer from your eyes/ears to your working memory isn’t as fast as it could be.
- Mental Clutter: Other thoughts or previous test sequences are getting in the way. (This is a big part of why numbers are often harder than words.)
If Your Score Is High
A high score is awesome, but let’s be clear about what it means.
- Skill, Not Just Biology: A score of 20+ with the Major System is a testament to practice and learning a technique. It’s an acquired skill, like playing guitar.
- The “Transfer” Problem: Being great at remembering number sequences doesn’t automatically make you great at remembering names, grocery lists, or where you left your keys. Memory is often task-specific.
What Should YOU Aim For?
Forget “higher is always better.” Set a useful target based on your life.
- For Everyday Life & Work: A reliable 9-11 digits is fantastic. It supports remembering phone numbers, short lists, and instructions without stress.
- For Students & Learners: Target 10-12 digits. This strengthens the working memory that helps you follow complex explanations and hold ideas in mind.
- For Gamers & Strategy Lovers: Aim for 12-14 digits with good consistency. This trains the rapid processing useful for in-game awareness.
- For Memory Hobbyists: The goal shifts to learning a system. Start by aiming for 15+ using our number memory techniques guide.
Quick Answers to Common Questions
Is 10 digits a good number memory score?
Yes, it’s solid. Isolid. f you did it without any tricks, it means your natural working memory is above average. If you used a simple strategy like chunking, it means you’re applying it well.
Is a score of 15 digits genius-level?
Usually not. solid. Scores around 15 almost always involve some kind of memory technique. It shows you’ve learned and practiced a useful skill, which is impressive in its own way, but it’s not a direct measure of innate intelligence.
Why does my score change every time I test?
This is completely normal. Working memory is affected by your energy, stress, focus, and even the time of day. It measures your current state, not your permanent potential. A variation of 2-3 digits is expected.
Ready to Understand Your Brain Better?
Now that you know what your score means, the logical next step is knowing how to improve it the right way. We’ve covered the “what” and “why” here.
Our dedicated guide covers the “how” with clear, actionable steps.
OR
Note: This content is for informational and self-improvement purposes. It is based on cognitive science principles and our platform data, but is not a medical or diagnostic tool.
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.



8 thoughts on “Good Number Memory Score: Average, Good & Best Digit Span”
Comments are closed.