How The Brain Ranks Patterns
Introduction:
Every second, your brain faces an impossible task: processing millions of sensory inputs while using minimal energy. The solution? A sophisticated pattern ranking system that determines:
- What deserves attention? — From noise to signal
- What should be ignored? — Efficient filtering
- What predicts danger or reward? — Survival priority
- What matches memory templates? Familiarity weighting
What completes an unfinished pattern? — Predictive completion
Core Insight: Your brain never receives the world “as it is.” Instead, it receives chaotic sensory data—millions of bits per second—and must rank that data in order of importance. This ranking system determines what you notice, remember, and act upon.

What “Ranking Patterns” Means in Neuroscience
Before a pattern is recognized, the brain must make critical decisions through automatic neural computation:
Key Ranking Mechanisms:
Familiarity Check: Does this pattern match a stored template? The brain compares incoming data against millions of stored patterns.
Relevance Assessment: Does it help predict something meaningful? Predictive value determines cognitive priority.
Urgency Detection: Could it signal threat, reward, or social importance? Survival circuits override everything else.
⚡ Consciousness Bottleneck: Only the top ~50–120 bits/sec reach conscious awareness. Ranking = prioritizing incoming patterns using neural weighting. This happens automatically through synaptic strength, neural gain control, prediction error minimization, dopamine-based value signals, and working memory gatekeeping.
Biological Evidence: This is why you hear your name in a noisy room (familiarity + relevance), notice faces in clouds (template matching), or instantly detect a threatening movement in your periphery (urgency override).
The Brain’s Pattern-Ranking Pipeline (Step-by-Step)
This pipeline is what NO competitor site explains clearly. Here’s the complete neural pathway:
Step 1: Sensory Input Filtering
Raw Data Stage: Eyes → 11 million bits/sec, but only a tiny fraction matters. The brain extracts edges, motion, color, and contrast. Nothing is meaningful yet—just raw features awaiting prioritization.
Step 2: Template Matching
Memory Comparison: The brain compares the new pattern to existing templates stored in the cortex. Matched → ranked higher. Unmatched → lower, unless novelty triggers surprise weighting.
Step 3: Prediction Coding
Prediction Engine: The brain checks, what pattern should appear next? Does the input confirm or break the prediction? High prediction → low priority. Surprise → high priority. This is why you instantly notice something “off.”
Step 4: Relevance Ranking
Value Assignment: Ranking is shaped by threat circuits (amygdala), reward circuits (dopamine), social importance, emotional tags, and frequency of exposure. Patterns tagged with reward, fear, or familiarity jump to the front.
Step 5: Attention & Working Memory
Final Selection: Only the top-ranked patterns enter working memory. Everything else is ignored. This is why working memory is not just capacity—it’s a scoreboard of prioritized patterns competing for consciousness.
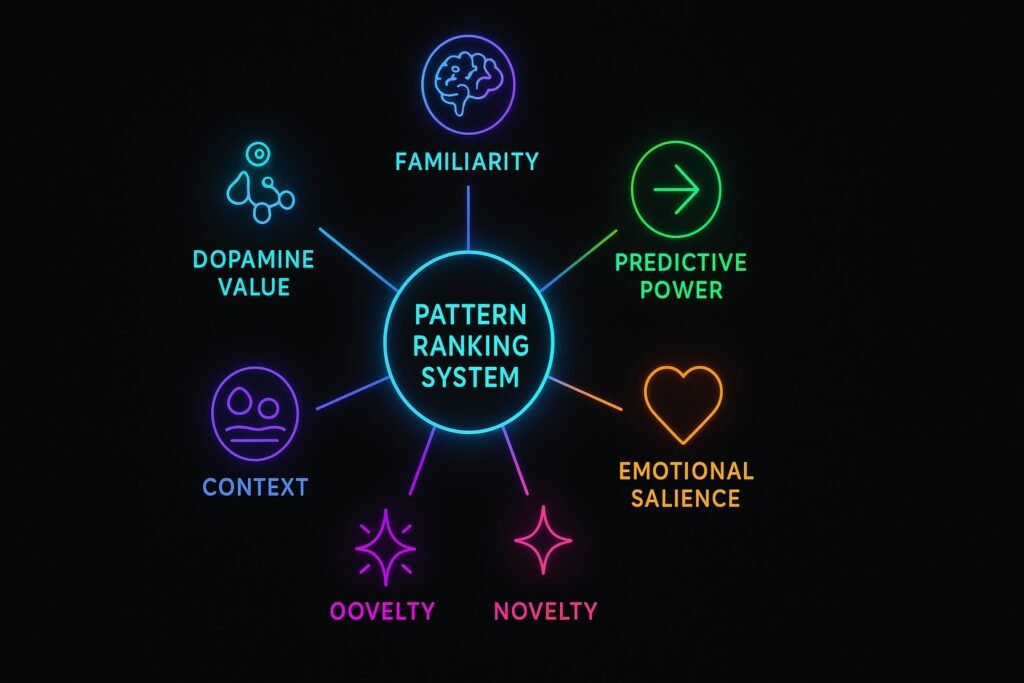

The Five Major Mechanisms The Brain Uses to Rank Patterns
1. Familiarity Ranking (Memory Weighting)
Patterns seen most often—faces, letters, and numbers—have stronger neural templates. Faster recognition, higher ranking, lower cognitive cost. This is why “expert brains” outperform beginners.
2. Prediction Power (Bayesian Processing)
Patterns that predict outcomes get priority. Footsteps predict arrival, tone predicts emotion, and gesture predicts intention. The brain rewards patterns that help with survival and understanding.
3. Emotional Salience (Amygdala Amplification)
Emotion amplifies pattern weight. Fear → very high priority. Reward → high. Neutral → low. This system evolved for survival: A snake-like pattern outranks everything.
4. Novelty Detection (Hippocampus CA 3)
The brain ranks “unexpected” patterns high. This triggers rapid learning. Novelty feels attention-grabbing because it signals potential learning opportunities.
5. Contextual Ranking (Environment-Based Weighting)
Example: A whisper in a library = high rank. The same whisper in traffic = low rank. Context dynamically rewrites the importance of patterns.
The Neural Circuit Behind Pattern Ranking
Visual Cortex (V1–V4)
Extracts features → groups them → sends proto-patterns upward. The entry point where raw visual data becomes candidate patterns.
Hippocampus (CA3 Pattern Completion)
Fills in missing pieces using memory templates. Seeing half a letter and instantly knowing it’s “A.” The pattern completion engine.
Prefrontal Cortex (PFC)
The Ranking Judge assigns meaning, importance, and decision value. Determines which patterns enter conscious thought.
Dopamine System
The Weight Modifier—Reward prediction error → increases synaptic strength. Shapes habit patterns, confidence levels, and prioritization.
Striatum
Manages routines and sequences: motor skills, habit memory, and procedural learning. Handles repetitive pattern ranking for efficiency.
The Brain’s Pattern Hierarchy Model (The 5-Level Rank Tree)
The brain categorizes patterns in layers, allowing it to “jump” from raw pixels to meaning within milliseconds:
Level 1: Features
Edges, angles, colors, and motion. Raw sensory building blocks awaiting assembly.
Level 2: Proto-objects
Shapes, clusters, contours. Features begin grouping into potential objects.
Level 3: Recognized Objects
Faces, numbers, letters, and animals. Full object recognition with identity.
Level 4: Concept Patterns
Intentions, categories, rules. Abstract understanding beyond physical form.
Level 5: Predictive Patterns
What will happen next? Future forecasting based on accumulated patterns.
How AI Ranks Patterns vs How The Brain Does
| Mechanism | Artificial Intelligence | Human Brain |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Method | Softmax probability ranking | Dopamine + synaptic weighting + prediction error |
| Learning Basis | Vector similarity, loss minimization, gradient descent | Synaptic plasticity, predictive coding, value-based attention |
| Emotion Integration | None (unless explicitly programmed) | Emotion-modulated weighting via amygdala |
| Energy Efficiency | High computational cost | Extremely energy-efficient (20W vs AI’s kW) |
| Adaptation Speed | Slow retraining required | Real-time adaptation via neuroplasticity |
💡 SEO & Content Insight: Understanding both systems enhances cognitive content and human-AI comparisons and creates richer articles that bridge neuroscience with technology trends.
How to Train Your Brain to Rank Patterns Better
1. Chunking Training
Allows faster grouping → higher ranking efficiency. Practice grouping related information into meaningful clusters.
2. Working Memory Workouts
Increases pattern bandwidth. Dual n-back games, memory span exercises, and complex task switching.
3. Expand Template Libraries
Read, study, and practice, and your brain forms stronger pattern maps. Expertise = dense neural templates.
4. Cognitive Clarity Drills
Reducing mental noise improves ranking accuracy. Mindfulness, focused attention training, and digital detox.
5. Deliberate Exposure + Testing
Seeing patterns repeatedly strengthens synaptic weights. Spaced repetition with active recall.
Conclusion: The Science of Pattern Priority
The brain ranks patterns based on a sophisticated multi-factor weighting system:
Familiarity—Frequently seen patterns get neural priority
Predictive Value—Patterns that forecast outcomes rise
Emotional Relevance—Fear and reward circuits amplify
Context—Environment dynamically reweights importance
Novelty—Unexpected patterns trigger learning mode
Reward Potential—Dopamine tags promising patterns
🧠 Foundation of Cognition: This ranking system is the foundation of intelligence, creativity, memory, problem-solving, social perception, and fast decision-making. Understanding it helps you train faster pattern detection, improve thinking, and build better cognitive skills.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does pattern recognition mean high IQ?
Not necessarily. High IQ individuals usually show stronger pattern ranking and faster prediction error correction, but pattern recognition can be trained through chunking, memory expansion, and exposure. Intelligence supports pattern use, not just pattern visibility.
How does the brain prioritize information?
The brain ranks signals using familiarity, emotional salience, predictive value, and context. Only top-ranked patterns enter conscious awareness or working memory through neural weighting and dopamine-based value signals.
Can you improve your pattern-recognition skills?
Yes—training working memory, practicing chunking, exposing your brain to varied tasks, and learning new skills all strengthen neural templates. Repeated exposure increases the speed and accuracy of pattern ranking.
Is pattern recognition the same as intuition?
Intuition is a fast, unconscious pattern ranking from accumulated experience. Pattern recognition is explicit awareness of structure; intuition is the brain ranking patterns before you’re aware of them.
Does dopamine affect how patterns are ranked?
Yes. Dopamine strengthens patterns linked to reward or prediction accuracy, increasing their importance and likelihood of being noticed or remembered. It acts as the brain’s natural ranking weight modifier.
Scientific References & External Sources
NIH—Superior Pattern Processing is the Essence of the Human Brain
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4141622/Nature—Scientists Map Neurological Patterns of Complex Thought
https://www.nsf.gov/news/scientists-map-neurological-patterns-complex-thoughtStanford University—The Hidden Pattern That Drives Brain Growth
https://news.stanford.edu/stories/2020/03/hidden-pattern-brain-growthMIT Picower Institute – Universal Pattern of Brain Wave Frequencies
https://picower.mit.edu/news/study-reveals-universal-pattern-brain-wave-frequencies
Master Your Pattern Recognition Skills
Apply the neuroscience of pattern ranking with our specialized tools and guides. Test your abilities, understand the science, and improve your cognitive performance.
Interactive Pattern Test
Challenge your brain's pattern ranking system in real-time with scientifically designed memory tests.
Take the TestComplete Pattern Guide
Understand pattern memory fundamentals and how it differs from visual memory processing.
Read GuideTraining & Improvement
Practical strategies to enhance your pattern recognition speed, accuracy, and overall ability.
Train NowDive deeper into pattern recognition science with our comprehensive resource library:
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.



1 thought on “How The Brain Ranks Patterns: Neuroscience of Pattern Prioritization”
Comments are closed.