How to Improve Verbal Memory
If you struggle to recall words, names, or instructions, you’re not alone. The good news is that verbal memory can be improved at any age. The secret isn’t more generic tips—it’s targeting the specific part of your memory process that needs work.
Before we dive into solutions, understand what verbal memory is by reading our guide What is Verbal Memory?. This guide gives you a clear, 7-day plan based on cognitive science. First, we’ll help you pinpoint your exact challenge using a simple diagnostic tree. Then, you’ll get targeted drills for that specific issue. It’s a practical, no-fluff approach that actually works.
The Quick Answer: Core Techniques
Here are the most effective techniques. The real improvement comes from using them systematically in the 7-day plan below.
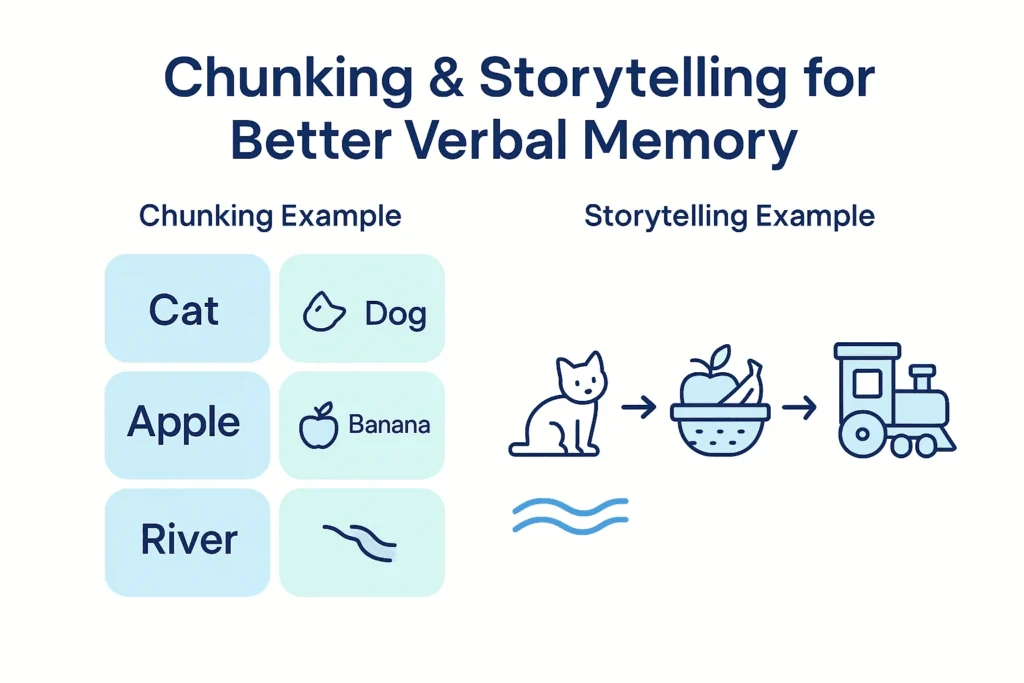
- Chunk Information: Break sentences or lists into groups of 3-5 words. Learn about visual techniques that can help.
- Engage Active Recall: Read aloud, summarize immediately, or use flashcards.
- Use Strategic Encoding: Link new words to vivid images, stories, or personal connections.
- Practice Retrieval Drills: Regularly test yourself without looking at the source.
- Employ Spaced Repetition: Review after 10 minutes, 1 day, then 3 days.
- Strengthen Foundational Habits: Prioritize sleep and manage stress to reduce attention blink.
Find Your Verbal Memory Problem
Most memory advice is one-size-fits-all. This simple decision tree helps you find your real bottleneck so you can fix it faster. If you’re also interested in other cognitive skills, check out our pattern recognition activities or number memory improvement guides.
Start Here: Which sounds most like you?
- Do words get “stuck on the tip of your tongue”?
If YES → Follow Path A: Word Retrieval. - Do you forget instructions or sentences almost immediately?
If YES → Follow Path B: Working Memory. - Do you remember now but forget after a day or two?
If YES → Follow Path C: Long-Term Storage. - Do lapses only happen under stress or pressure?
If YES → Follow Path D: Stress & Attention. - Want general improvement?
Follow Path E: Baseline Upgrade.
Targeted Solutions: Follow Your Path
Each path below addresses a different cognitive mechanism. Focus on the one from your diagnosis. For comparison with other memory types, see Working Memory vs. Short-Term Memory.
Path A: Fix Word Retrieval
The Problem: The word is in your memory, but you can’t access it. This is a retrieval block, not memory loss. This is similar to issues some people face with number recall.
Simple Fixes:
- Semantic Cueing: Think of related words or the category.
- Phonological Cuing: Go through the alphabet for the first sound.
- Context Re-creation: Mentally return to where you learned it.
3-Minute Daily Drill: Look at 5 objects, name them, and look away. After 30 seconds, try to recall them. Use the cues above if stuck. Learn more about this in our article Why We Forget Words.
Path B: Strengthen Working Memory
The Problem: Your brain’s “mental scratchpad” gets overloaded quickly. This is especially challenging for those with ADHD and working memory limits.
Simple Fixes:
- Chunking: Group information (like phone numbers: 123-456-7890).
- The Echo Technique: Silently repeat information for 10-15 seconds.
- Backward Recall: Try repeating a short list backward.
5-Minute Daily Drill: Have someone read a 10-12 word sentence. Repeat it back exactly. Stanford’s guide on Strategies for Improving Working Memory confirms these methods.

Path C: Boost Long-Term Storage
The Problem: Information doesn’t stick because of weak encoding or lack of review. Some people naturally excel at this—learn about why some have better memory.
Simple Fixes:
- One-Sentence Summary: Summarize anything you read/hear in one sentence.
- Teach-Back Method: Explain the concept to yourself like a teacher.
- Spaced Repetition: Review after 1 hour, 1 day, and 1 week.
Simple Daily Drill: Read a short article. Write 3 key terms. One hour later, write what you recall about them without looking. This also helps with reading-based memory improvement.
Path to D: Manage Stress & Attention
The Problem: Stress hormones block retrieval pathways. Your memory is temporarily offline. This affects athletic performance too.
Simple Fixes:
- Pre-emptive Breathing: 30 seconds of deep breaths before you need to recall.
- Single-Task Focus: When listening, just listen. Put distractions away.
- Sleep Priority: Memory consolidates during deep sleep.
This is related to how stress affects your reaction time vs. reflex time and can cause gaming delays.
Path E: Baseline Upgrade
For general improvement: Rotate through these micro-habits for well-rounded verbal memory enhancement.
Daily Habits:
- Read Aloud for 2 Minutes: Sync visual and auditory encoding.
- Practice Story Linking: Create quick narratives to connect items.
- Do Fast Recall Rounds: Name as many items in a category as possible in 60 seconds.
- Explore Other Memory Types: Try pattern memory training or number memory techniques.
Your 7-Day Verbal Memory Plan
| Day | Focus | Core Activity | Duration | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Diagnosis | Use the memory tree and establish your baseline | 15 min | Get your starting point |
| Day 2 | Active Encoding | Practice “One-Sentence Summary” three times | 5–10 min | Strengthen initial learning |
| Day 3 | Working Memory | Chunking and backward recall drills | 10 min | Expand mental capacity |
| Day 4 | Retrieval Practice | Test yourself on Day 2 material without looking | 10 min | Forge stronger recall paths |
| Day 5 | Spaced Repetition | Quick quiz on material from Days 2–4 | 15 min | Fight the forgetting curve |
| Day 6 | Integration | Listen to a podcast, summarize, recall after 5 minutes | 12 min | Combine skills under mild pressure |
| Day 7 | Assessment | Review progress and lock in one drill as a habit | 20 min | Measure progress & build routine |


How to Track Your Progress
Seeing improvement keeps you motivated. Track these simple metrics. For other cognitive measurements, see what constitutes a good number memory score.
- Streak Length: How many items can you recall in a row?
- Recall Accuracy: What percentage do you remember correctly after a delay?
- Retrieval Speed: How fast do the right words come to mind?
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Passive Re-reading: This feels productive but is weak compared to active recall.
- Multitasking While Learning: Divided attention ruins deep encoding. Multitasking harms cognitive performance.
- Cramming: One long session is less effective than spaced practice, as NIH research shows.
- Ignoring Cognitive Limits: Understand brain storage limits to set realistic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is poor verbal memory normal?
Yes. It varies naturally and fluctuates with stress, fatigue, and practice levels. Some variability is explained by why people differ in cognitive skills.
Can adults really improve?
Absolutely. Your brain’s neuroplasticity allows for improvement at any age with consistent practice. Even reaction time can be improved with training.
How long to see results?
Most people notice better recall speed and accuracy within 2 to 3 weeks of consistent drills.
Is this related to exceptional memory abilities?
While this guide focuses on normal improvement, you might be interested in eidetic memory or chimpanzee memory studies.
Is this related to dementia?
This guide is for cognitive self-improvement, not diagnosis. For memory problems that affect daily life, consult a doctor.
Disclaimer: MemoryRush content is for informational and self-improvement purposes only, based on cognitive science. It is not medical advice. For medical concerns, please consult a healthcare professional.
Final Word
Improving verbal memory is about smart, targeted practice—not harder work. Use the diagnostic tree to find your real bottleneck, follow the 7-day plan to build momentum, and track your progress. Your ability to remember words and ideas isn’t fixed. With this clear system, you can make it stronger.
Explore More: If you found this helpful, you might also enjoy our guides on the Chimp Test, pattern vs visual memory, or understanding different reaction times.
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.


3 thoughts on “How to Improve Verbal Memory”
Comments are closed.