Pattern Memory vs Visual Memory
Understanding how we remember things is key to unlocking the potential of our cognitive processes. Two types of memory often confuse us: pattern memory and visual memory. Both terms are frequently used interchangeably, but they refer to distinct aspects of how our brains function. This article will clearly define these memory types, explain their differences, and help you identify which type you rely on most.
Core Difference in One Sentence
- Visual Memory: Refers to remembering what you saw.
- Pattern Memory: Involves remembering how things were arranged.
Although both rely on vision, the way the brain processes and stores these memories varies significantly. Understanding these differences can help you enhance your memory by identifying which system works best for you.
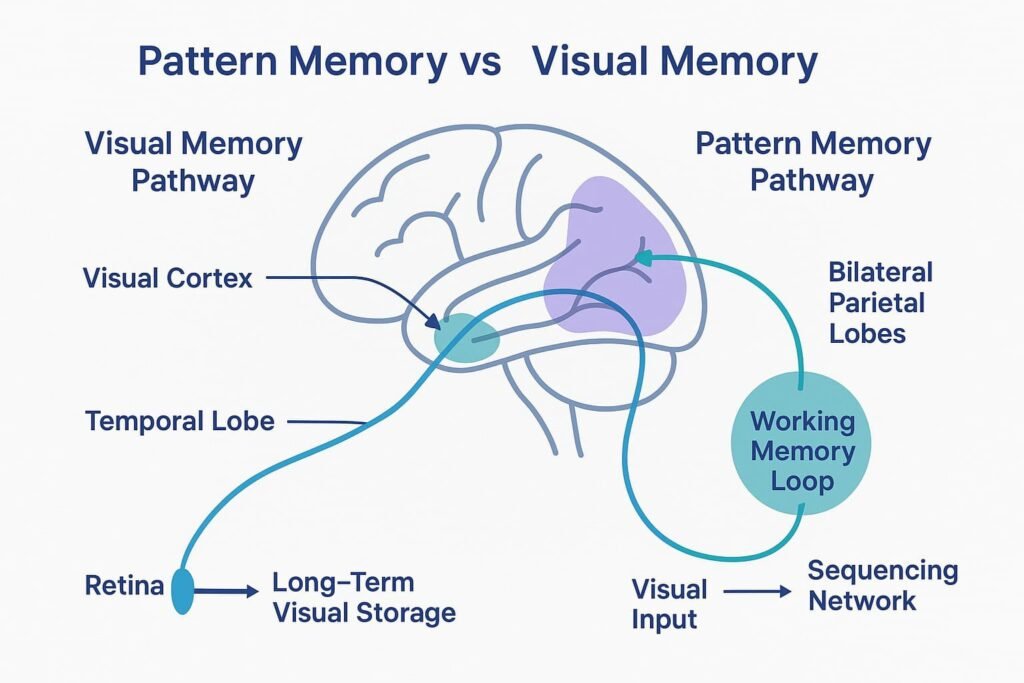

What Is Visual Memory?
Visual memory is the ability to recall images, scenes, faces, and other visual details. This type of memory allows you to recognize things you’ve seen before and store these images for later use.
- What it stores: Images, faces, scenes, written words.
- Memory type: Recognition-based (e.g., recognizing a face in a crowd).
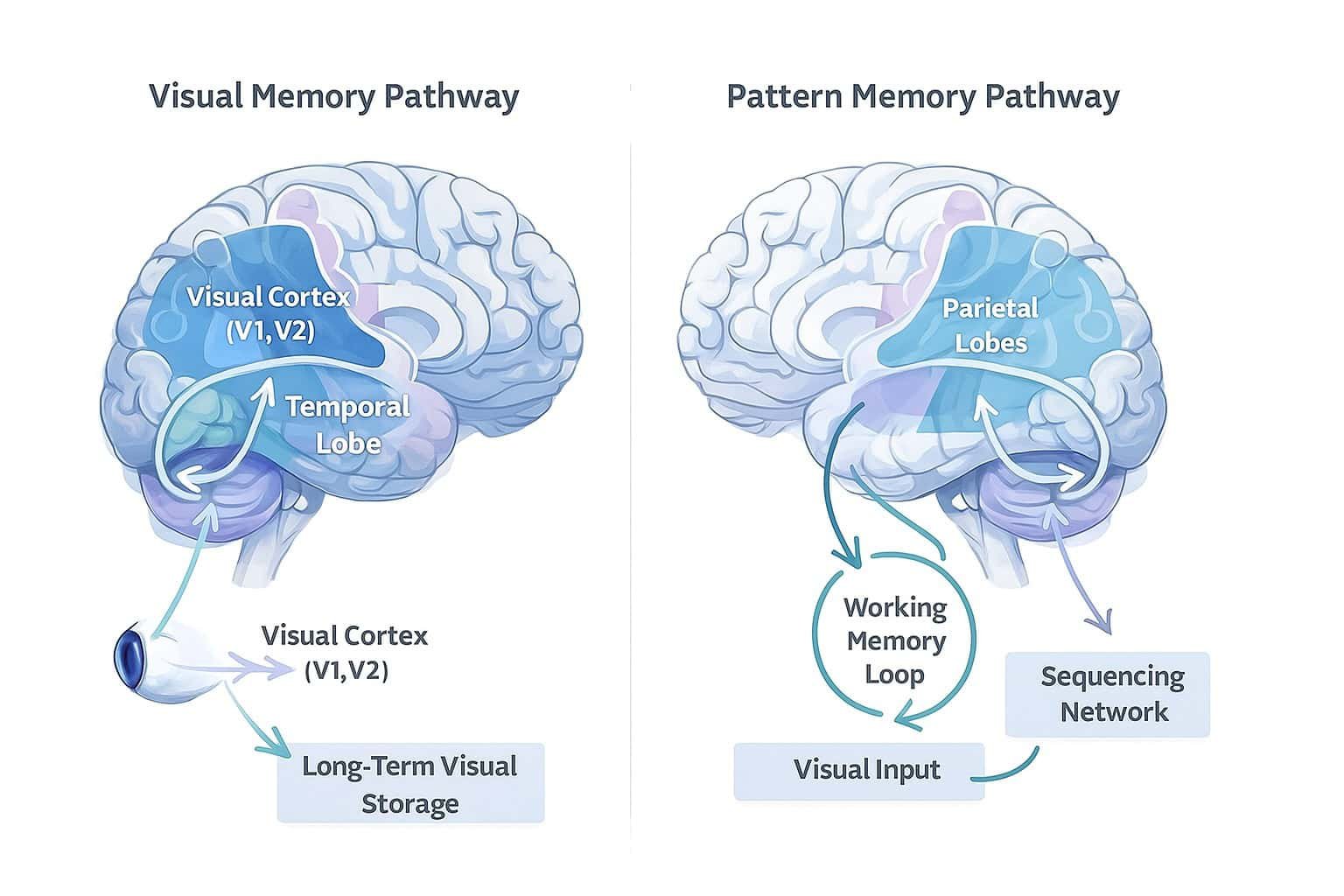
- Brain regions involved: Primarily the occipital and temporal lobes.
- Examples:
- Recognizing a face: You can easily identify someone you’ve seen before.
- Recalling a room layout: You remember the arrangement of furniture in a room.
- Remembering a logo: Recognizing a brand’s logo even after seeing it once.
Visual memory helps you retrieve detailed images or scenes and is critical in daily tasks like identifying familiar faces or navigating a room. It plays a crucial role in how we interact with the visual world around us.
Still unsure about which memory type you use the most? Take our interactive memory type quiz to discover whether you’re more visual or pattern-oriented. See how it matches with your everyday tasks!
Discover Your Memory Type
Take this interactive decision tree to find out which memory type you primarily use
• YES: I easily recall faces, places, or images I've seen before, like remembering someone's face from a meeting or recognizing a store logo.
• NO: I struggle to recall specific images, but I remember the patterns or sequences of things instead.
This quiz helps you understand your memory preferences and boost cognitive awareness
| Aspect | Visual Memory | Pattern Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Images & scenes | Order & structure |
| Depends on | Recognition | Sequencing |
| Brain Area | Occipital + Temporal | Parietal |
| Fails when | Details blur | Order breaks |
| Used in | Face recall, layout recall | Number / grid tasks, passwords, routines |
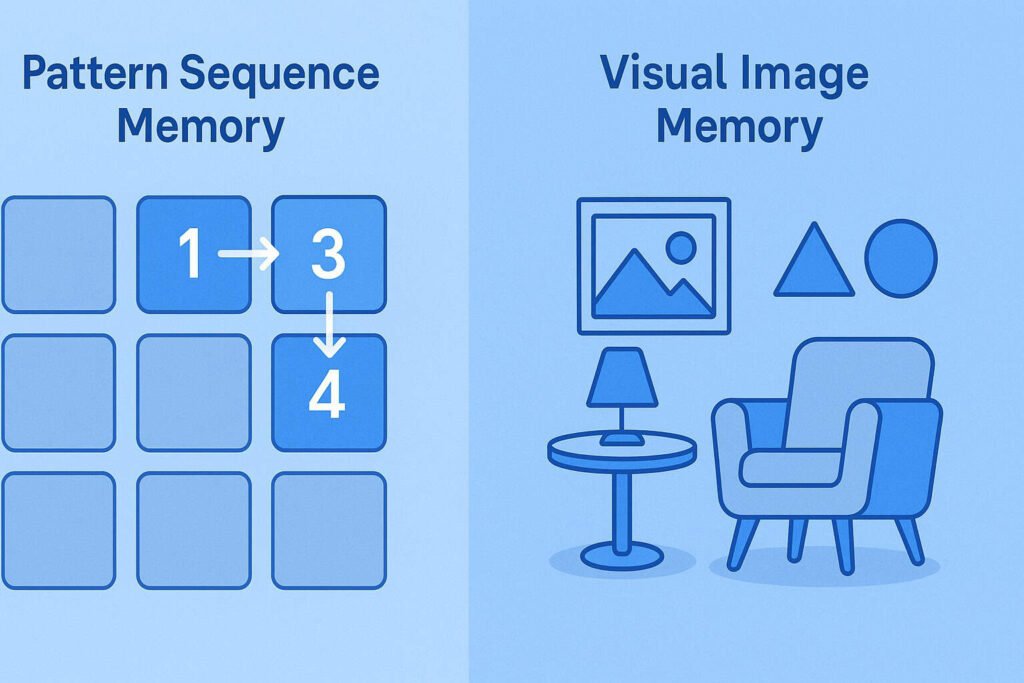

Where Each Memory Type Is Used in Daily Life
- Visual Memory:
- Recalling faces of people you’ve met.
- Navigating to your favorite café by remembering its layout.
- Recognizing logos on advertisements.
- Pattern Memory:
- Recalling the sequence of numbers in a phone number.
- Remembering the pattern of keys on a keyboard.
- Following a routine in your daily life (e.g., your morning routine).
Ever wondered how your memory impacts your everyday tasks? Explore how both visual memory and pattern memory play a role in activities like driving, reading, or even remembering numbers!
Common Misunderstandings
Why do people often confuse pattern memory with visual memory? The main reason is that both types of memory are involved in seeing and visualizing things. However, their roles are very different:
- Tests often mix both types of memory, leading to confusion.
- Misuse of language: Terms like “visual” are often used broadly, without distinguishing between remembering what you saw and remembering how things were arranged.
FAQs
- Is pattern memory part of visual memory?
- Pattern memory is a subset of visual memory but focuses on structure and order rather than visual detail.
- Can someone be good at both?
- Yes, people can use both visual and pattern memory, but one might dominate based on the task.
- Why am I bad at remembering images but good at sequences?
- This may indicate that you are more pattern memory dominant, as you remember arrangements and sequences more easily than individual images.
- Does ADHD affect visual or pattern memory differently?
- ADHD can affect working memory, which includes both pattern and visual memory, but the impact can vary based on the individual’s cognitive profile.
Key Takeaways
- Visual memory is primarily about remembering content: images, faces, places, and objects.
- Pattern Memory is about remembering structure: order, sequences, or spatial relationships.
- Both are controlled by different brain systems.
- Use the decision tree to determine which type of memory you rely on more in daily tasks.
Want to boost your memory skills further? Check out our detailed guides on improving pattern memory
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.


6 thoughts on “Pattern Memory vs Visual Memory”
Comments are closed.