

Simple vs Choice Reaction Time (SRT vs CRT)
Quick Answer:
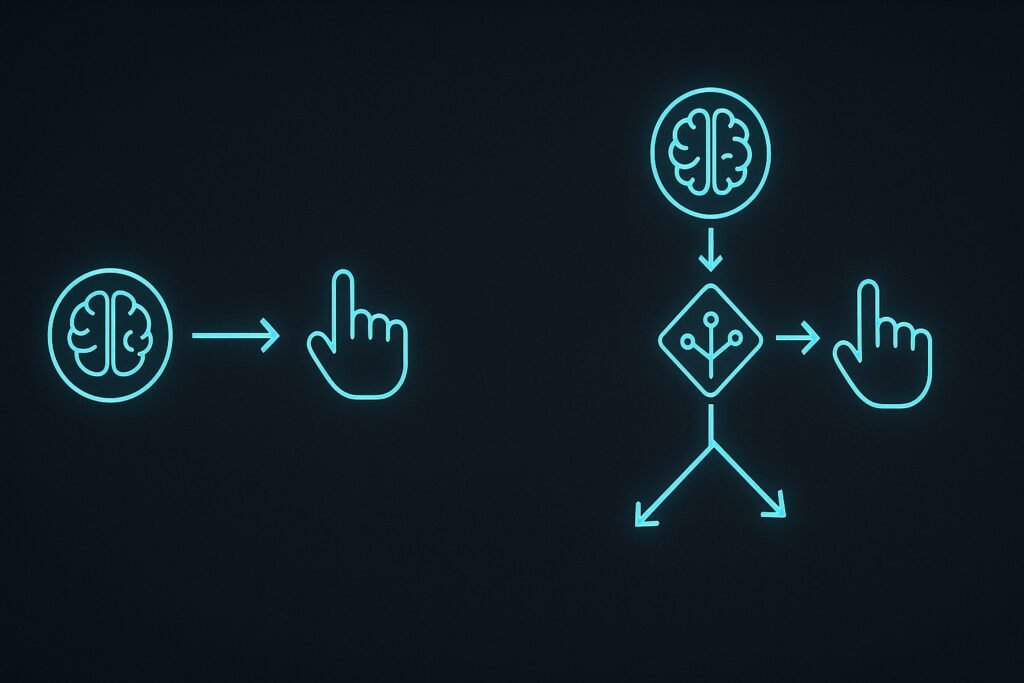
Reaction time measures how quickly your brain processes information and initiates responses. Simple Reaction Time (SRT) involves responding to one stimulus with one action, while Choice Reaction Time (CRT) requires distinguishing between multiple possible stimuli and selecting appropriate responses. This distinction represents fundamental differences in cognitive processing, with CRT typically being 70-200 milliseconds slower due to decision-making requirements.
Understanding these differences is essential for athletes, gamers, drivers, UX designers, and cognitive researchers. This comprehensive guide covers the neuroscience, applications, measurement methods, and improvement strategies for both reaction time types.
Test Your Reaction Time Now
Want to measure your own SRT and CRT? Try our scientifically-designed reaction time test that measures both simple and choice reaction times with precise millisecond accuracy.
What Is Reaction Time?
Reaction time measures the interval between stimulus presentation and response initiation. This cognitive metric reflects processing efficiency across attention, perception, decision-making, and motor control systems. Different reaction time paradigms assess distinct cognitive abilities, with SRT representing basic processing speed and CRT evaluating decision-making capabilities.
Related: Understand the key differences between reaction time vs reflex time and how they impact performance in different scenarios.
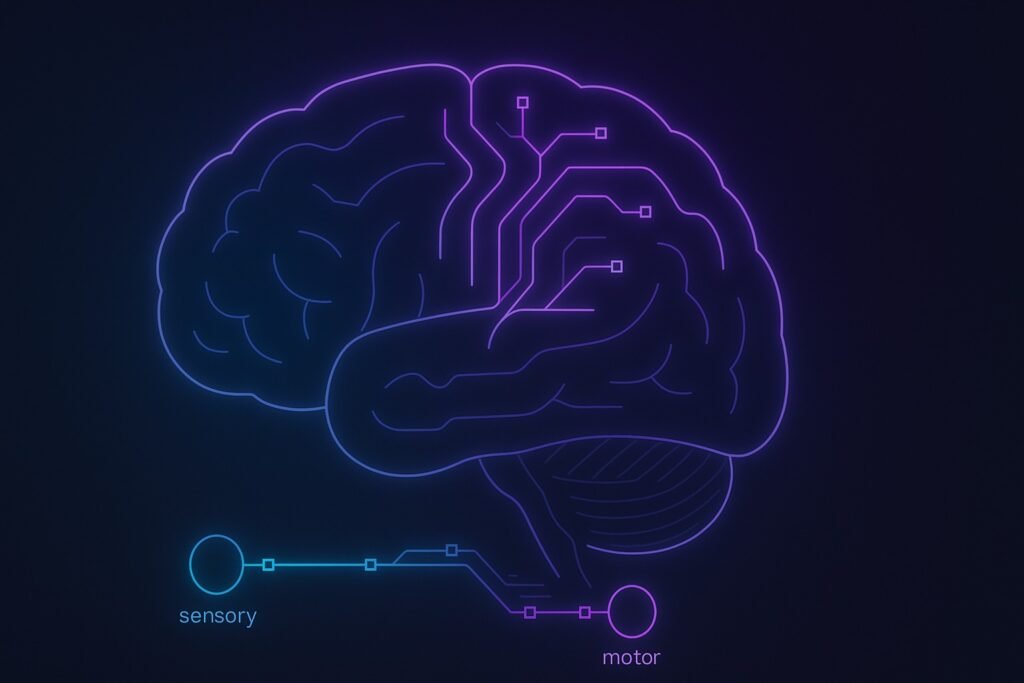
Simple Reaction Time (SRT)
Simple Reaction Time is the fastest form of human response, involving automatic reactions to predictable stimuli without decision-making requirements. This pure sensory-motor pathway provides baseline measurements of neural conduction speed and processing efficiency.
- 200-250ms Visual SRT
- 140-190ms Auditory SRT
- 130-180ms Tactile SRT
Neuroscience Behind SRT
SRT represents the shortest neural pathway: sensory detection → perceptual processing → motor command → physical response. Every step is pre-loaded in the brain with zero decision-making, making this the fastest reaction humans can perform.
Real-Life SRT Examples
Sports
100m sprint start (gun → run), table tennis serve response, boxing punch defense with single cues, cricket batsman pre-reaction. Learn more about reaction time in sports and how elite athletes train this skill.
Driving
Traffic light turns green → accelerate, responding to horn sounds. SRT forms the foundation of basic driving responses that keep you safe on the road.
Gaming
Flick shots when targets pop up, reaction to predictable enemy actions. If you’re wondering why your reaction time feels delayed when gaming, it could be SRT variations.
Everyday Life
Phone ringing → pick it up, someone calling your name → turn. These automatic responses rely on your brain’s simplest processing pathways.
Learn: Discover what constitutes good reaction time across different age groups and activity levels.
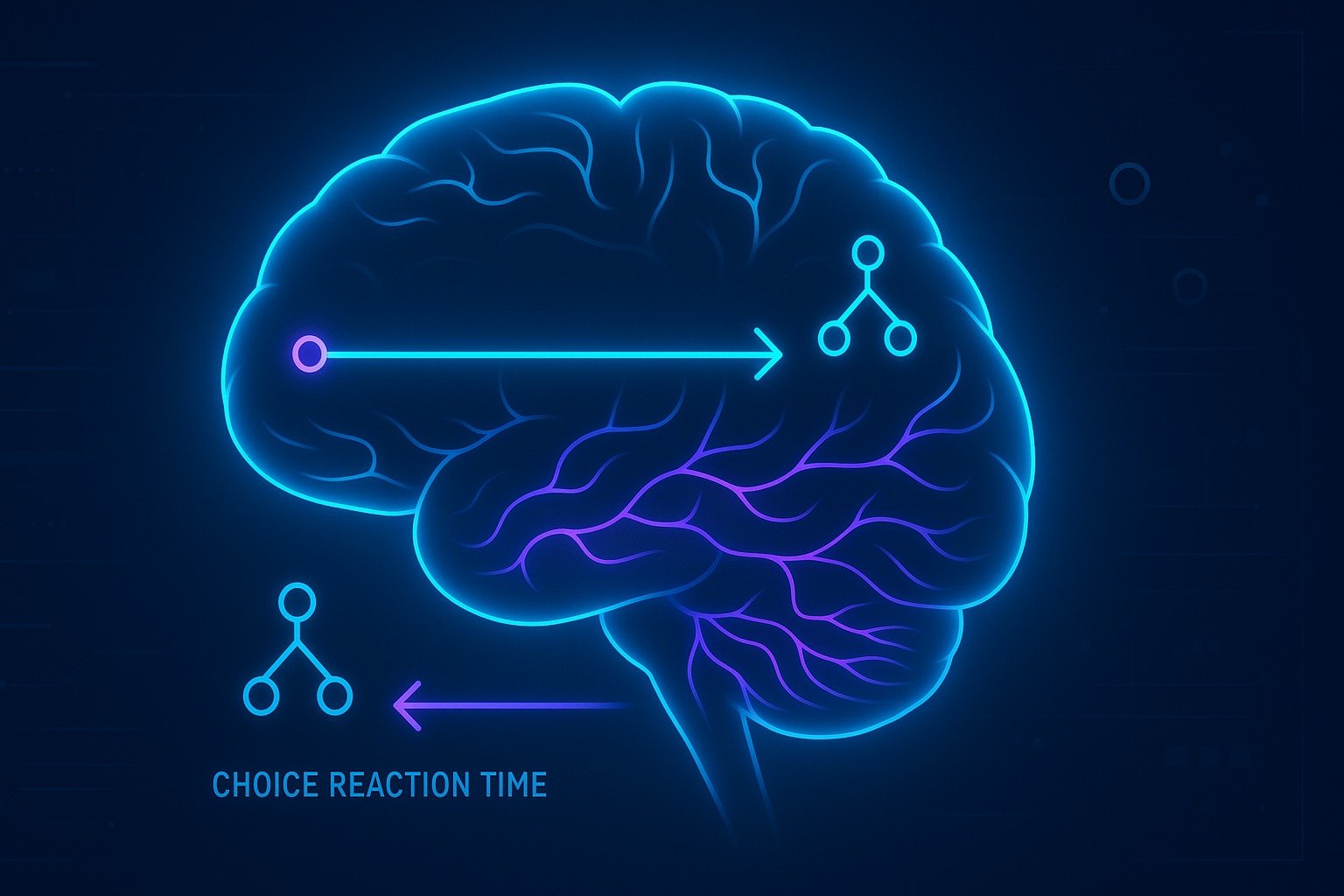
Choice Reaction Time (CRT)
Choice Reaction Time involves stimulus discrimination and response selection, requiring additional cognitive processing that naturally slows reaction times. This paradigm assesses decision-making quality, cognitive flexibility, and working memory efficiency under time pressure.
Why CRT is Slower Than SRT
Step 1: Detection
Same as SRT – initial stimulus detection
Step 2: Discrimination
Brain must identify “What exactly did I see/hear?”
Step 3: Selection
Choose correct motor response for specific signal
Step 4: Execution
Execute chosen movement
Hick’s Law: More Choices = Slower Reaction Time
Hick’s Law explains why CRT increases as the number of choices increases. Reaction time increases logarithmically with more options as the brain needs extra time to interpret, compare, and decide.
Related: Wondering why your reaction time is slow? CRT is particularly sensitive to fatigue, stress, and cognitive load.
SRT vs CRT: Complete Scientific Comparison
| Feature | Simple Reaction Time (SRT) | Choice Reaction Time (CRT) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Stimuli | 1 | 2+ |
| Possible Responses | 1 | 2+ |
| Decision-Making Required |   |
  |
| Typical Speed | 200-250ms (visual) | 300-500ms (2-8 choices) |
| Cognitive Load | Low | High |
| Brain Regions Involved | Sensory + Motor cortices | Prefrontal + Parietal + Motor cortices |
How to Measure Reaction Time
Reaction time can be measured using multiple standardized tasks. Each evaluates different cognitive mechanisms: sensory speed, attention, motor control, decision-making, and inhibition.
Simple Reaction Time Test
- Measures pure sensory → motor response speed with no decision-making.
- Single stimulus appears (light, beep) and you perform one fixed action.
Expected: 200-250ms (visual), 140-190ms (auditory). Test your SRT now
Choice Reaction Time Test
- Measures decision-making speed with stimulus discrimination.
- Multiple stimuli mapped to different actions.
Expected: 300-500ms depending on complexity. Test your CRT now
Go/No-Go Test
- Measures impulse control and response inhibition.
- Respond to some stimuli, withhold response to others.
- Used for ADHD testing and impulse control research
4-Choice & 8-Choice Test
- Advanced CRT measuring multi-option decision speed and Hick’s Law curve accuracy.
- Used in military selection and high-level esports analysis
Stroop Test
- Measures cognitive interference and attention control.
- Say color of word, not the word itself.
- Massive interference effect slows reaction time
Home Testing Methods
Beginner: Online tests, phone apps, ruler-drop test
Advanced: Gaming aim trainers, VR modules, EEG-based systems
Norms for Healthy Adults
| Age | Typical SRT | Typical CRT |
|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | 200-250ms | 300-400ms |
| 26-35 | 210-260ms | 320-420ms |
| 36-50 | 230-280ms | 350-450ms |
| 50+ | 250-300+ms | 380-550+ms |
Real-World Applications
Sports Performance
Elite athletes rely on both SRT and CRT. SRT dominates automatic responses like sprint starts, while CRT determines success in reading opponent movements and making strategic decisions. Learn more about reaction time in sports and training methods.
Esports & Gaming
Competitive gaming is 99% Choice Reaction Time. FPS games require decisions like shoot vs reposition, fighting games involve reading mix-ups, and MOBAs require counter-action selection. A 70-120ms difference in CRT can decide wins. If you’re experiencing delayed reaction time in gaming, it’s likely CRT issues.
Driving Safety
Driving is almost entirely CRT, not SRT. CRT determines whether you correctly choose brake vs swerve for pedestrians, interpret multiple road signs, and react to sudden lane changes.
Aging & Cognitive Decline
SRT stays relatively stable while CRT declines significantly starting around age 40-50 due to reduced prefrontal cortex function. CRT is used in early dementia screening.
ADHD, Sleep, Stress & Cognitive Load
ADHD often shows normal SRT but slower CRT. Sleep deprivation dramatically affects CRT. Stress reduces PFC efficiency, and multitasking can ruin reaction time by increasing CRT by 100-200ms.
Improve Your Reaction Time
Ready to enhance your reaction speed? Our comprehensive guide covers evidence-based strategies for improving both SRT and CRT through targeted training, lifestyle adjustments, and cognitive exercises.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Choice Reaction Time (CRT) slower than Simple Reaction Time (SRT)?
What is a good reaction time for adults?
How can I improve my reaction time naturally?
Does reaction time decline with age?
How does ADHD affect reaction time?
Is faster reaction time always better?
What’s the difference between recognition and choice reaction time?
Why do gamers focus on reaction time training?
Does caffeine improve reaction time?
Can stress slow reaction time?
Ready to Test and Improve?
Now that you understand the difference between SRT and CRT, put your knowledge into practice. Test your reaction time, compare with records, and start improving today.
Scientific References & External Resources
- American Psychological Association. (2022). Reaction Time. APA Dictionary of Psychology. https://dictionary.apa.org/reaction-time
- Simply Psychology. (2023). Cognitive Load Theory. https://www.simplypsychology.org/cognitive-load-theory.html
- Verywell Mind. (2023). Attention and Focus. https://www.verywellmind.com/attention-and-focus-2795009
- Frontiers in Psychology. (2023). Decision-Making Research. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology
- National Institutes of Health. (2021). Reaction Time & Aging Study. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.