What Is a Good Reaction Time?
Quick Answer:
A good reaction time typically falls between 150 and 250 milliseconds (ms), depending on the type of stimulus and the individual. Visual reaction times are generally slower than auditory or tactile responses. Times closer to 150–200 ms are considered strong for everyday tasks, while slower responses often reflect fatigue, distraction, or age-related changes.
What “Good” Reaction Time Actually Means
Reaction time is an essential measure of how quickly our brain and body can respond to a stimulus. A “good” reaction time is typically defined as a response that falls within a range that supports efficient neural processing for a given task. However, the interpretation of what constitutes “good” varies depending on the task, the type of stimulus, and individual factors such as age and training.
For instance, reaction times that are slower than 250 ms often indicate issues such as fatigue or distraction, while faster responses are typically indicative of higher attentiveness or specialized training. It’s important to understand that a “good” reaction time is context-dependent and differs for visual, auditory, and tactile stimuli. Therefore, a reaction time considered excellent for one activity may be normal for another.

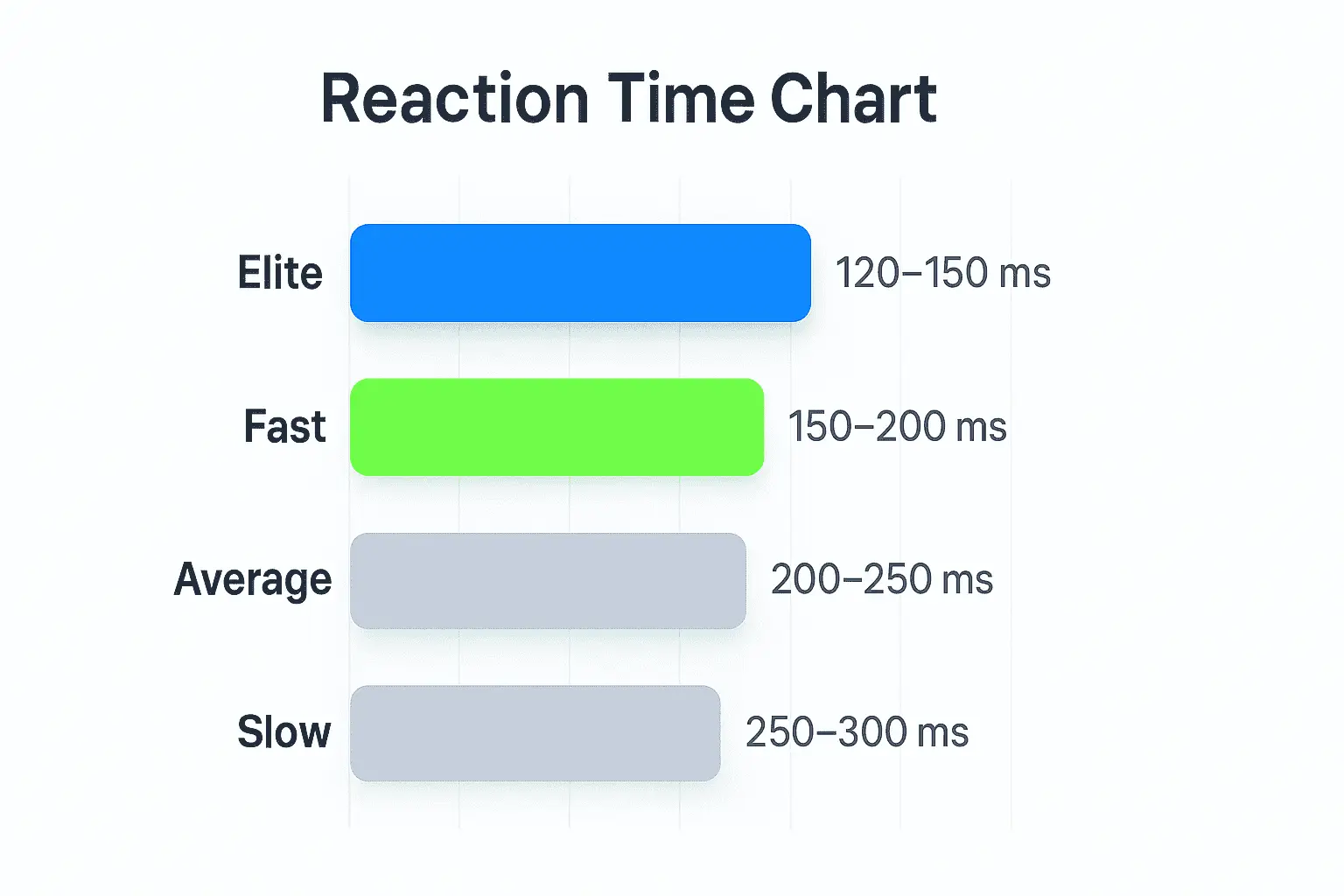
Reaction Time Ranges (General Benchmarks)
| Category | Typical Range (ms) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Elite | 120–150 | Exceptional, rare consistency |
| Fast | 150–200 | Very good, high attentional efficiency |
| Average | 200–250 | Normal adult range |
| Slow | 250–300 | Often fatigue/distraction related |
| Very Slow | 300+ | Reduced alertness or interference |
Reaction Time Depends on the Type of Stimulus
Reaction time can differ based on the type of stimulus presented. Below is a brief breakdown of how various stimuli impact reaction time:
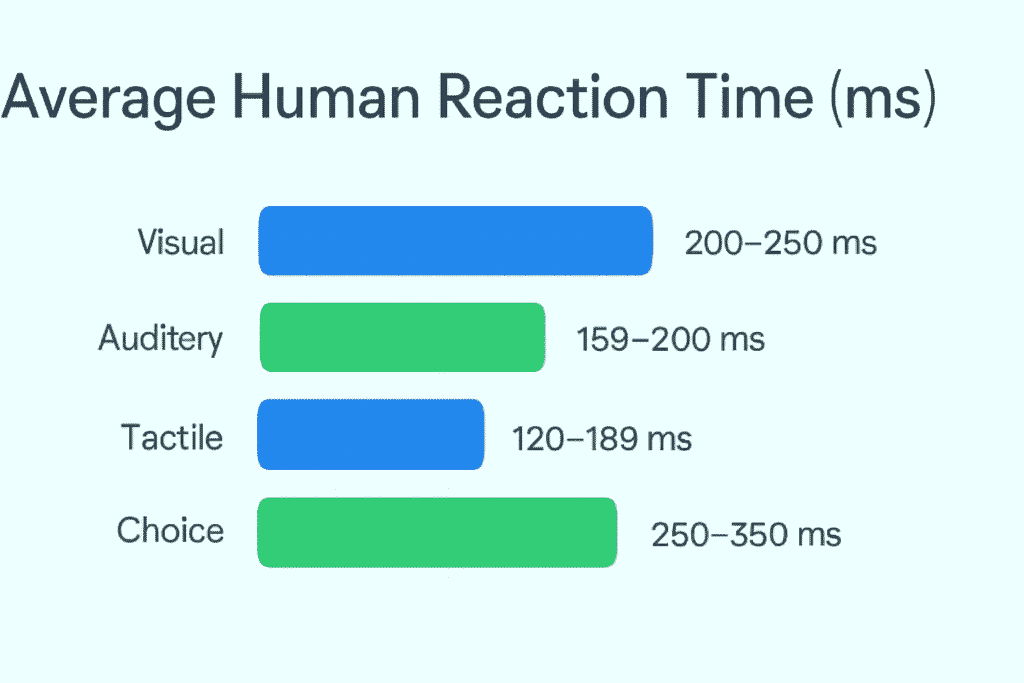
- Visual Stimulus: Typically the slowest. It takes more time for the brain to process visual information as compared to other sensory inputs.
- Auditory Stimulus: Faster than visual, as sound is processed quicker in the brain’s auditory cortex.
- Tactile Stimulus: The fastest form of reaction time as the tactile signals are processed by the somatosensory cortex, often requiring less cognitive effort to interpret.
This variance occurs because each sensory pathway has different processing speeds, and the brain’s ability to react depends on the type of input it receives.

Why Reaction Time Varies Between People
Several factors contribute to why reaction time can differ from one person to another. Understanding these factors can provide insights into why some individuals may exhibit faster or slower responses than others:
- Attention Stability: Individuals with more consistent focus can respond quicker to stimuli.
- Fatigue: Tiredness slows down neural processing, leading to longer reaction times.
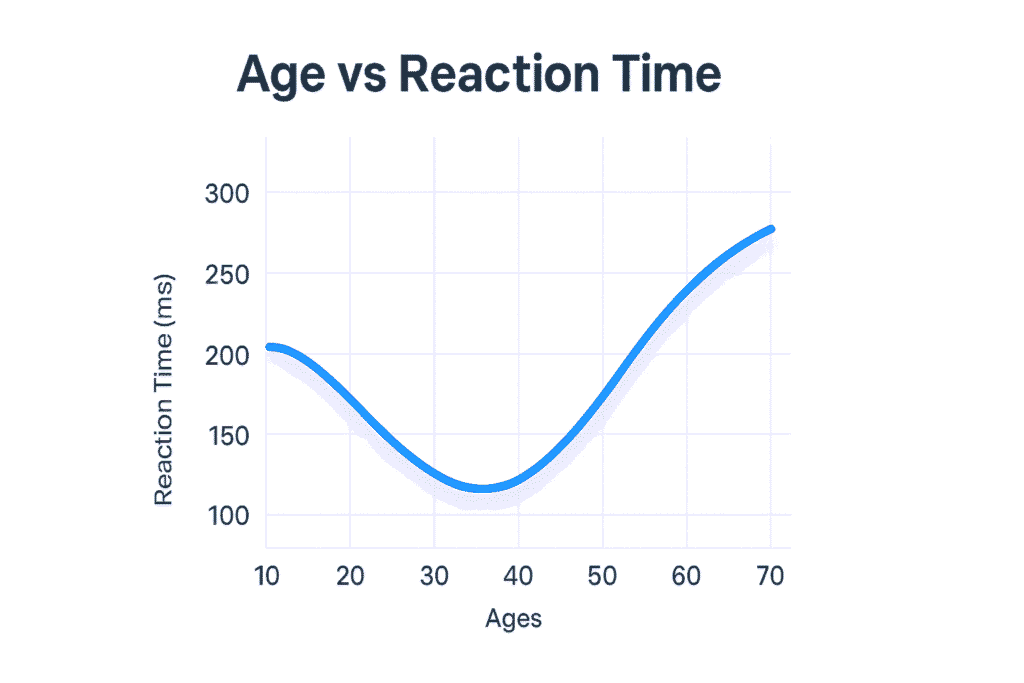
- Age: As we age, reaction times generally tend to increase due to natural biological processes.
- Measurement Method: Different testing devices and environments can introduce latency, influencing results.
- Device/Input Latency: Technology, such as the input lag from screens or gaming controllers, can add milliseconds to the reaction time.
These factors influence not only the baseline reaction time but also how an individual performs over time or under different conditions.

How Reaction Time Is Measured
Reaction time measurement involves a simple setup:
- Stimulus Appears: A visual, auditory, or tactile stimulus is presented to the subject.
- Timer Starts: As soon as the stimulus is perceived, the individual begins their response.
- Response Ends Timer: The reaction time is concluded when the response is executed (such as pressing a button or making a movement).
There are two primary types of reaction time:
- Simple Reaction Time: A single stimulus is presented, and the individual must react in a predetermined way (e.g., pressing a button when a light flashes).
- Choice Reaction Time: The individual must choose between multiple responses based on the stimulus (e.g., pressing one button for a red light and another for a green light).
What This Page Does NOT Cover
This page is focused on defining what counts as good reaction time. It does not delve into the following topics:
- ❌ How to improve reaction time – For training tips, refer to How to Improve Reaction Time →
- ❌ Reaction time vs reflex time – A detailed comparison can be found at Reaction Time vs Reflex Time →
- ❌ Fastest reaction time ever recorded – Check out Fastest Reaction Time Ever →
- ❌ Reaction time in gaming or sports – Separate dedicated pages for those topics are available.
- ❌ Clinical angles or ADHD-related content – These are explored in specialized articles.
This section serves as a boundary to keep the content clear and focused on its core purpose—providing benchmarks for what is considered good reaction time.
FAQs
- Is 200 ms a good reaction time?
Yes, 200 ms is generally considered a good reaction time for most tasks, and it falls within the average range for adults. - Is 150 ms fast?
Yes, 150 ms is considered fast and is typically observed in elite athletes or highly trained individuals. - What is the average human reaction time?
The average human reaction time is typically around 250 ms for visual stimuli. - Does age affect reaction time?
Yes, reaction time tends to slow down gradually with age, particularly after the age of 30. - Why does reaction time change day to day?
Factors like fatigue, attention, stress, and distractions can cause day-to-day fluctuations in reaction time.
Conclusion
To summarize, a good reaction time typically falls between 150 and 250 ms, depending on factors like stimulus type and age. Context matters: what’s considered a “good” reaction time for a gamer may differ from what’s ideal in a sports setting.
If you’re curious about where you fall within these ranges or want to test your reaction time, consider trying a Cognitive Assessment to measure your performance accurately.
External Sources
Trusted research and medical resources about reaction time and cognitive performance
Touheed Ali
Touheed Ali is the founder and editor of MemoryRush, an educational cognitive science platform. He builds and maintains interactive tools focused on memory, attention, and reaction time.
His work centers on translating established cognitive science concepts into clear, accessible learning experiences, with an emphasis on transparency and responsible design.
MemoryRush
Educational Cognitive Science Platform • Memory • Attention • Reaction Time
Educational Use Only
MemoryRush is created for learning and self-exploration and does not provide medical, psychological, or clinical evaluation.



5 thoughts on “What Is a Good Reaction Time? Discover the Best Benchmarks & Tips”
Comments are closed.